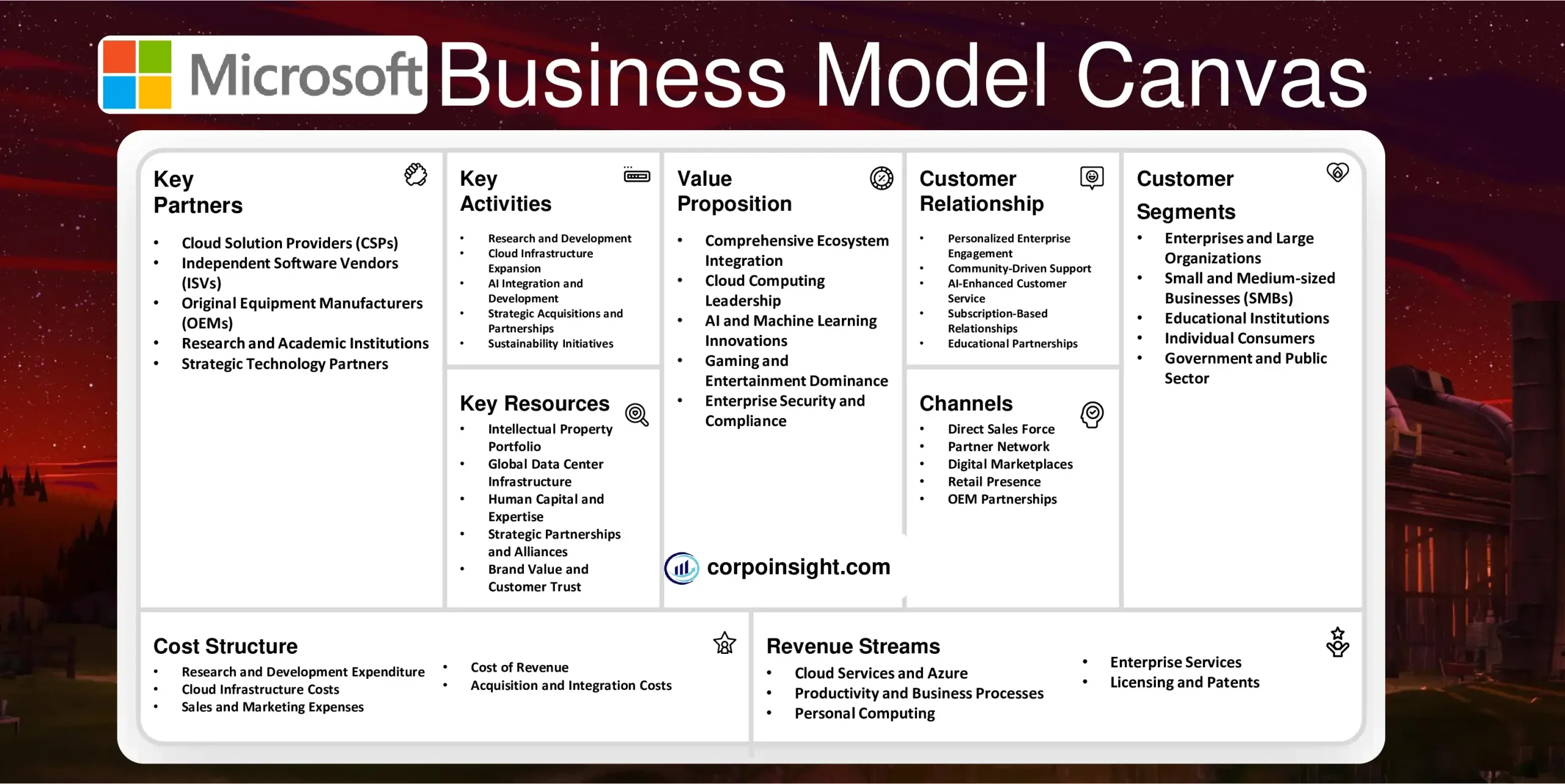
Microsoft Business Model Canvas 2024
Microsoft, a tech giant founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen in 1975, has revolutionized personal computing and software development, evolving from its humble beginnings to become a multinational corporation that shapes the digital landscape through its operating systems, cloud services, and innovative hardware solutions. In this Microsoft Business Model Canvas, I will identify its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting fact!
In 1994, Microsoft removed the popular game Minesweeper from Windows in China at the government’s request because it violated a ban on digital content containing mines.
Microsoft Competitors
Apple | Google | Amazon | IBM | Oracle | Salesforce | Sony | Samsung | Dell | AdobeCop
Customer Segments – Microsoft Business Model Canvas

Enterprises and Large Organizations: Microsoft caters to Fortune 500 companies and multinational corporations, offering comprehensive solutions like Microsoft 365, Azure cloud services, and Dynamics 365; for instance, Coca-Cola utilizes Microsoft’s cloud platform to enhance its supply chain operations, while Walmart leverages Azure for its e-commerce infrastructure.
Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs): Through products like Microsoft 365 Business and Azure SMB solutions, Microsoft addresses the needs of growing companies that require scalable, cost-effective technology; a notable example is how many local retailers have adopted Microsoft Teams for internal communication and collaboration during the shift to remote work.
Educational Institutions: From K-12 schools to universities, Microsoft provides tailored solutions such as Microsoft Education and Azure for Students; for example, the University of Central Florida uses Microsoft Teams and OneNote to facilitate remote learning and enhance student collaboration across its large, diverse student body.
Individual Consumers: While often overlooked, Microsoft maintains a strong presence in the consumer market through products like Windows OS, Xbox gaming consoles, and Surface devices; the success of Xbox Game Pass, which surpassed 25 million subscribers in 2022, exemplifies Microsoft’s ability to engage individual consumers in the competitive gaming industry.
Government and Public Sector: Microsoft offers specialized solutions for government agencies and public sector organizations, ensuring compliance with stringent security and privacy regulations; the U.S. Department of Defense’s adoption of Microsoft’s cloud services for its Joint Enterprise Defense Infrastructure (JEDI) project showcases the company’s capabilities in this sector.
Value Proposition – Microsoft Business Model Canvas

Comprehensive Ecosystem Integration: Microsoft offers a seamlessly integrated ecosystem of products and services, enabling users to work efficiently across devices and platforms; for example, the Microsoft 365 suite allows seamless collaboration between Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, while also integrating with Teams for communication, thereby enhancing productivity for both individuals and organizations.
Cloud Computing Leadership: Through Azure, Microsoft provides scalable, secure, and cost-effective cloud solutions that empower businesses to innovate and grow; notably, as of 2023, Azure held over 20% of the global cloud market share, second only to Amazon Web Services, and has been adopted by 95% of Fortune 500 companies for various cloud computing needs.
AI and Machine Learning Innovations: Microsoft incorporates cutting-edge AI technologies across its product range, from Copilot in Microsoft 365 to advanced Azure AI services; for instance, the company’s partnership with OpenAI has led to the integration of GPT-4 technology into various Microsoft products, significantly enhancing user productivity and decision-making capabilities.
Gaming and Entertainment Dominance: With Xbox and the acquisition of major gaming studios like Activision Blizzard, Microsoft offers unparalleled gaming experiences and content; Xbox Game Pass, which surpassed 25 million subscribers in 2022, provides access to a vast library of games, demonstrating Microsoft’s commitment to value in the entertainment sector.
Enterprise Security and Compliance: Microsoft’s comprehensive security solutions, including Microsoft Defender and Azure Security Center, address the complex cybersecurity needs of modern organizations; for example, the company’s Zero Trust security model has been widely adopted by enterprises, with Microsoft reporting a 50% year-over-year increase in Zero Trust solution deployments in 2023.
Revenue Streams – Microsoft Business Model Canvas

Cloud Services and Azure: Microsoft’s cloud platform, Azure, has become a major revenue driver, competing strongly with Amazon Web Services; in fiscal year 2023, Intelligent Cloud segment revenue, which includes Azure, reached $87.9 billion, growing 22% year-over-year and showcasing the increasing demand for cloud computing solutions across industries.
Productivity and Business Processes: This segment, encompassing Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365), LinkedIn, and Dynamics 365, continues to be a significant revenue source; in FY 2023, it generated $69.3 billion, with Microsoft 365 Commercial revenue growing by 16%, reflecting the ongoing digital transformation in workplaces and the value businesses place on integrated productivity tools.
Personal Computing: Windows OEM, devices, gaming, and search advertising fall under this category; despite facing challenges in the PC market, this segment generated $54.6 billion in FY 2023, with Xbox content and services revenue growing by 7%, underscoring Microsoft’s strong position in the gaming industry and its ability to diversify within personal computing.
Enterprise Services: Microsoft’s consulting and support services, tailored for large organizations, contribute significantly to its revenue; although specific figures are not always broken out, these services are crucial for maintaining long-term relationships with enterprise clients and often lead to increased adoption of other Microsoft products and services.
Licensing and Patents: While not always highlighted, Microsoft earns substantial revenue from licensing its technologies and patents to other companies; for instance, the company has long-standing patent licensing agreements with Android device manufacturers, which, although declining in recent years, still contribute to the company’s diverse revenue streams.
Channels – Microsoft Business Model Canvas

Direct Sales Force: Microsoft’s enterprise-focused sales team plays a crucial role in securing large contracts and maintaining relationships with key clients; for instance, in 2023, this channel was instrumental in closing a multi-year, multi-billion dollar deal with AT&T for cloud services, demonstrating the effectiveness of direct engagement with high-value customers.
Partner Network: The Microsoft Partner Network, comprising over 400,000 organizations globally, serves as a vital channel for reaching diverse markets; these partners, ranging from small IT consultancies to large system integrators like Accenture, contributed to over 95% of Microsoft’s commercial revenue in 2023, highlighting the significance of this ecosystem in Microsoft’s go-to-market strategy.
Digital Marketplaces: Microsoft’s digital storefronts, including the Microsoft Store for consumers and Azure Marketplace for businesses, have become increasingly important channels; notably, the Azure Marketplace saw a 70% year-over-year increase in transacted sales in 2023, reflecting the growing preference for self-service procurement of cloud solutions and software.
Retail Presence: While scaled back in recent years, Microsoft maintains a strategic retail presence through its Experience Centers and partnerships with major retailers; for example, the flagship Microsoft Experience Center in New York City not only showcases products but also serves as a hub for customer education and brand engagement, complementing the company’s online sales channels.
OEM Partnerships: Microsoft’s longstanding relationships with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) like Dell, HP, and Lenovo remain a critical channel for distributing Windows and other software; in 2023, despite a challenging PC market, OEM partnerships helped maintain Windows’ dominant position with over 75% market share in desktop operating systems.
Customer Relationships – Microsoft Business Model Canvas

Personalized Enterprise Engagement: Microsoft maintains deep relationships with enterprise clients through dedicated account managers and tailored solutions; for example, the company’s Enterprise Advantage program, which saw a 15% increase in adoption in 2023, offers personalized support and strategic planning sessions, enabling large organizations like Coca-Cola to optimize their use of Microsoft technologies across complex global operations.
Community-Driven Support: Microsoft fosters a robust community of users and developers through platforms like Microsoft Learn and GitHub; notably, the Microsoft Learn platform reported over 50 million unique visitors in 2023, while GitHub, acquired by Microsoft in 2018, surpassed 100 million developers, demonstrating the company’s commitment to nurturing a self-sustaining ecosystem of knowledge sharing and collaboration.
AI-Enhanced Customer Service: Leveraging its AI capabilities, Microsoft has significantly improved its customer service experiences; the implementation of AI-powered chatbots and virtual agents across its support channels has led to a 30% reduction in average resolution time for customer queries in 2023, while maintaining a high customer satisfaction rate of 92%.
Subscription-Based Relationships: Microsoft’s shift towards subscription-based models, particularly with Microsoft 365 and Azure, has transformed its customer relationships into ongoing partnerships; this approach not only provides steady revenue but also allows for continuous engagement, as evidenced by the 25% year-over-year increase in Microsoft 365 consumer subscribers, reaching 63 million in 2023.
Educational Partnerships: Microsoft maintains strong relationships with educational institutions through programs like Microsoft Imagine Academy and Azure for Students; in 2023, these initiatives reached over 200 million students globally, fostering loyalty among future professionals and decision-makers while supporting educational institutions in their digital transformation journeys.
Key Activities – Microsoft Business Model Canvas

Research and Development: Microsoft’s commitment to innovation is evident in its substantial R&D investments, which reached $24.5 billion in fiscal year 2023; this focus on cutting-edge technologies has led to breakthroughs in areas such as quantum computing, where Microsoft’s Azure Quantum service has attracted partnerships with leading research institutions and corporations seeking to explore quantum applications.
Cloud Infrastructure Expansion: Continual development and expansion of Azure’s global infrastructure remain a key activity, with Microsoft adding new data centers and regions to meet growing demand; in 2023, the company announced plans to build 50 to 100 new data centers each year, significantly outpacing its competitors and enabling Azure to offer lower latency and enhanced data residency options to its customers worldwide.
AI Integration and Development: Microsoft’s strategic focus on AI integration across its product portfolio has intensified, with the company’s AI and Research division growing by 25% in 2023; this activity has resulted in significant enhancements to products like Microsoft 365 Copilot, which leverages GPT-4 technology to boost productivity, and has been adopted by over 60% of Fortune 500 companies within its first year of release.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships: Microsoft continues to strengthen its market position through strategic acquisitions and partnerships; the completion of the Activision Blizzard acquisition in 2023, valued at $68.7 billion, not only bolstered Microsoft’s gaming division but also provided valuable assets for metaverse development, demonstrating the company’s commitment to shaping future digital experiences.
Sustainability Initiatives: As part of its corporate responsibility efforts, Microsoft has intensified its focus on sustainability, pledging to be carbon-negative by 2030; in 2023, the company reported a 17% reduction in its carbon emissions year-over-year and invested $1 billion in carbon removal technologies, showcasing its commitment to environmental stewardship as a key business activity.
Key Resources – Microsoft Business Model Canvas

Intellectual Property Portfolio: Microsoft’s vast intellectual property holdings, including over 95,000 active patents as of 2023, serve as a critical resource for innovation and competitive advantage; this extensive portfolio not only protects Microsoft’s technologies but also generates significant licensing revenue, with patent licensing agreements contributing an estimated $3.5 billion to the company’s annual revenue.
Global Data Center Infrastructure: Microsoft’s expansive network of data centers, encompassing over 200 facilities across 60+ regions worldwide by 2023, forms the backbone of its cloud services; this infrastructure, representing an investment of more than $15 billion annually, enables Azure to offer low-latency, high-availability services to customers globally, while also supporting the company’s ambitious sustainability goals through innovative cooling and power management technologies.
Human Capital and Expertise: With a workforce of approximately 220,000 employees as of 2023, including some of the world’s top engineers, data scientists, and AI researchers, Microsoft’s human capital is arguably its most valuable resource; the company’s ability to attract and retain top talent is evidenced by its consistent ranking among the top 5 most desirable workplaces globally, according to LinkedIn’s annual reports.
Strategic Partnerships and Alliances: Microsoft’s extensive network of partnerships, including over 400,000 partner organizations globally, serves as a crucial resource for market reach and innovation; notable examples include the deepening partnership with OpenAI, which has allowed Microsoft to integrate cutting-edge AI capabilities across its product line, and collaborations with industry leaders like SAP and Adobe to deliver integrated enterprise solutions.
Brand Value and Customer Trust: Microsoft’s brand, valued at approximately $278 billion in 2023 according to Interbrand, represents a significant intangible resource; this strong brand equity, built on decades of trust and reliability, enables Microsoft to maintain its position as a leader in enterprise software and cloud services, with over 95% of Fortune 500 companies using Azure and a customer retention rate exceeding 90% for its enterprise services.
Key Partners – Microsoft Business Model Canvas

Cloud Solution Providers (CSPs): Microsoft’s network of over 90,000 Cloud Solution Providers plays a crucial role in extending the reach of Azure and Microsoft 365; for instance, Rackspace, a leading CSP, reported a 30% year-over-year increase in Microsoft cloud services revenue in 2023, demonstrating the symbiotic relationship between Microsoft and its cloud partners in driving adoption and providing tailored solutions to end-users.
Independent Software Vendors (ISVs): The Microsoft Partner Network includes thousands of ISVs who develop applications and services that integrate with or run on Microsoft platforms; notable examples include Salesforce, which deepened its integration with Microsoft Teams in 2023, resulting in a 40% increase in joint customers, and Adobe, whose Creative Cloud suite saw enhanced interoperability with Microsoft 365, leading to a 25% boost in shared enterprise adoptions.
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): Microsoft’s longstanding partnerships with OEMs like Dell, HP, and Lenovo remain critical for the distribution of Windows and related hardware; in 2023, despite a challenging PC market, these partnerships helped maintain Windows’ dominant position with over 75% market share in desktop operating systems, while also driving innovation in form factors such as foldable and dual-screen devices.
Research and Academic Institutions: Collaborations with universities and research organizations fuel Microsoft’s innovation pipeline; for example, the company’s quantum computing partnership with the University of Sydney, announced in 2023, aims to develop practical quantum algorithms, while its AI for Accessibility program has partnered with over 200 organizations globally to create AI solutions for people with disabilities.
Strategic Technology Partners: Microsoft’s alliances with other tech giants create powerful synergies; the ongoing partnership with OpenAI, strengthened by a multi-billion dollar investment in 2023, has enabled Microsoft to integrate advanced AI capabilities across its product suite, while the collaboration with Oracle, which saw a 50% increase in joint cloud customers in 2023, offers enterprises seamless integration between Azure and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Cost Structure – Microsoft Business Model Canvas

Research and Development Expenditure: Microsoft’s commitment to innovation is reflected in its substantial R&D spending, which reached $27.3 billion in fiscal year 2023, representing approximately 12% of its revenue; this significant investment, focused on areas such as AI, cloud computing, and quantum technologies, not only drives product development but also helps maintain Microsoft’s competitive edge in rapidly evolving tech landscapes.
Cloud Infrastructure Costs: The expansion and maintenance of Microsoft’s global data center network for Azure constitute a major cost center, with the company investing over $15 billion annually in cloud infrastructure; these costs, while substantial, are offset by economies of scale and technological efficiencies, such as the implementation of AI-driven cooling systems that have reduced energy consumption by 15% in new data centers.
Sales and Marketing Expenses: Microsoft’s global sales and marketing efforts, crucial for maintaining its market position, accounted for $22.7 billion in fiscal year 2023; this expenditure, which includes costs associated with the Microsoft Partner Network and direct sales force, has seen a shift towards digital channels, resulting in a 10% reduction in per-customer acquisition costs while maintaining growth across key product lines.
Cost of Revenue: This category, which includes manufacturing and distribution costs for products, datacenter operations, and content creation for gaming, totaled $64.2 billion in FY 2023; notably, Microsoft’s strategic shift towards cloud services has altered this cost structure, with datacenter operations becoming an increasingly significant component, growing at a rate of 20% year-over-year.
Acquisition and Integration Costs: Microsoft’s strategy of growth through acquisitions incurs significant costs, both in terms of purchase prices and subsequent integration efforts; for example, the $68.7 billion acquisition of Activision Blizzard in 2023 not only represented a major capital outlay but also entailed substantial integration costs, estimated at over $1 billion for system alignments and workforce restructuring.
Summary of Microsoft Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on Microsoft Business Model Canvas
Microsoft’s Business Model Canvas reveals a robust and diversified strategy that has positioned the company as a leader in the technology sector. By leveraging its strong brand, extensive partner network, and substantial R&D investments, Microsoft has successfully transitioned from a primarily software-focused company to a cloud and AI powerhouse. Its integrated ecosystem of products and services, coupled with a customer-centric approach, enables Microsoft to serve diverse market segments while maintaining a strong financial position and driving continuous innovation across multiple technology frontiers.

I’m Samin Yasar, currently working as a Brand Strategist for one of the world’s leading Prop Firms. I have a passion for content creation and dream of making my own film one day.



