Venmo Business Model Canvas 2025: Trusted, Trendy, and Thriving
Revolutionizing the way friends split bills and transfer money, Venmo has become a ubiquitous digital wallet that not only simplifies transactions but also adds a social twist to financial interactions. In this Venmo Business Model Canvas, we will identify its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting fact!
The company was acquired by Braintree for $26.2 million in 2012, just a year after its full launch.
Venmo Competitors
PayPal | Cash App | Zelle | Apple Pay | Google Pay | Samsung Pay | Stripe | Square | Wise (formerly TransferWise) | Revolut
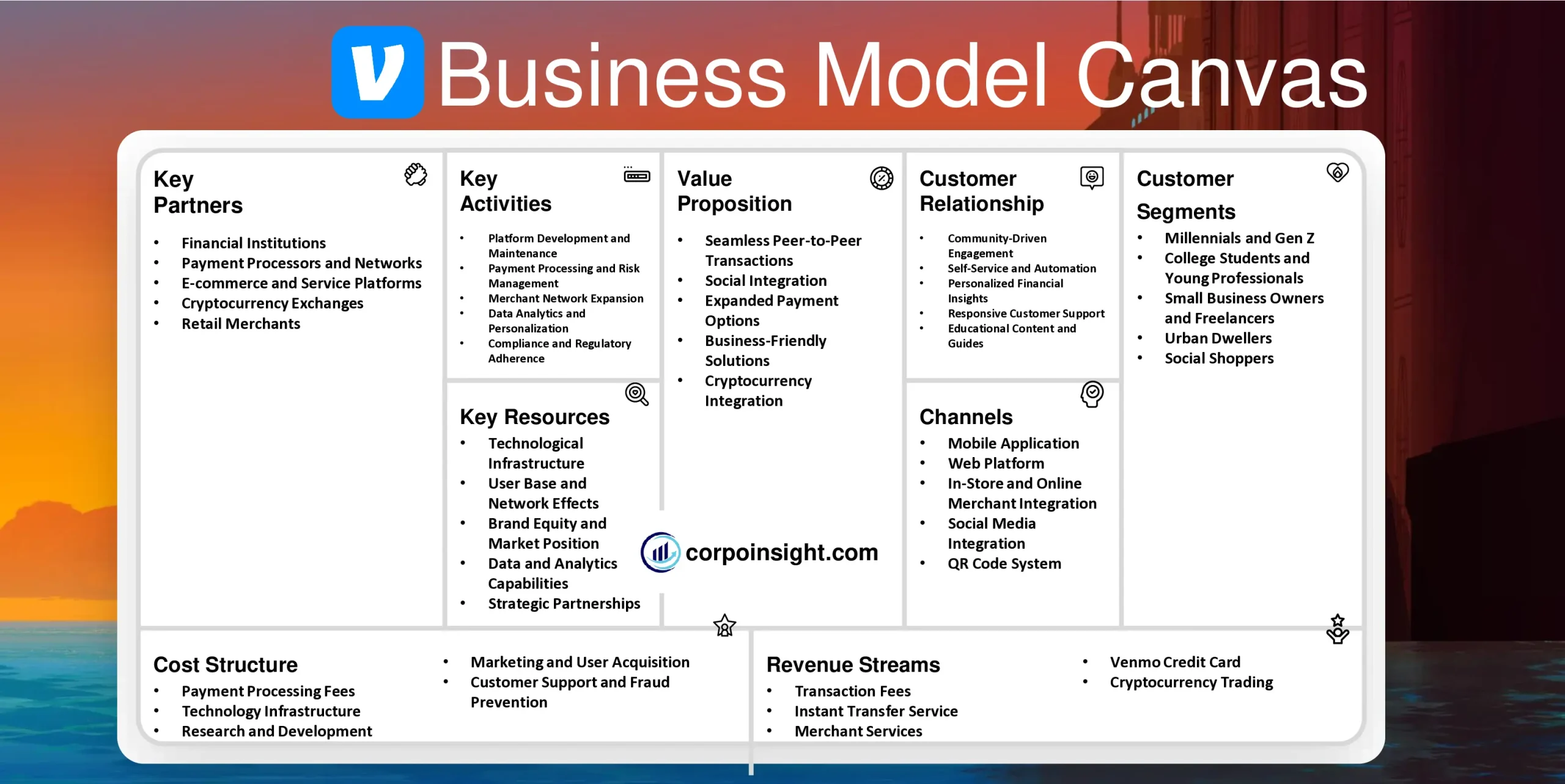
Customer Segments – Venmo Business Model Canvas

Millennials and Gen Z: These generations, born between 1981 and 2012, constitute Venmo’s primary user base, with millennials alone accounting for over 60% of users. Their tech-savvy nature and preference for digital solutions make them ideal adopters of Venmo’s peer-to-peer payment platform.
College Students and Young Professionals: A significant portion of Venmo’s user base comprises individuals aged 18-34, particularly college students and young professionals who frequently engage in shared expenses. This demographic values the app’s ease of use for splitting costs related to rent, utilities, dining out, and group activities.
Small Business Owners and Freelancers: With the introduction of Venmo for Business in 2020, the platform has attracted a growing segment of small business owners and freelancers. These users leverage Venmo’s popularity among younger consumers to facilitate payments for goods and services, thereby expanding their customer base.
Urban Dwellers: Venmo usage is particularly high in urban areas, where the population density and lifestyle foster frequent social interactions and shared expenses. City residents, who often engage in activities like dining out, attending events, or sharing transportation costs, find Venmo’s platform especially useful for managing these financial exchanges.
Social Shoppers: A unique segment of Venmo users is individuals who view financial transactions as social experiences. These users appreciate the app’s social feed feature, which allows them to share and comment on transactions, thus blending financial management with social networking in a way that appeals to their desire for connectivity and transparency.
Value Proposition – Venmo Business Model Canvas

Seamless Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Venmo’s primary value lies in its ability to facilitate instant, frictionless money transfers between individuals, which has revolutionized how people split bills, share expenses, and exchange funds; this convenience has led to the app processing over $230 billion in payments annually as of 2022.
Social Integration: By incorporating a social feed that allows users to share and comment on transactions (with privacy controls), Venmo has transformed financial exchanges into social interactions, appealing to millennials and Gen Z users who value transparency and connectivity in their digital experiences.
Expanded Payment Options: Venmo has broadened its value proposition by introducing features like the Venmo debit card and credit card, which not only allow users to make purchases directly from their Venmo balance but also earn cashback rewards, thus creating a more comprehensive financial ecosystem for its user base.
Business-Friendly Solutions: With the launch of Venmo for Business in 2020, the platform now offers value to small businesses and freelancers by providing a popular payment option for younger consumers; this expansion has allowed Venmo to tap into the growing gig economy and e-commerce sectors.
Cryptocurrency Integration: Recognizing the increasing interest in digital currencies, Venmo has added cryptocurrency buying, selling, and holding capabilities, which not only diversifies its offerings but also positions it at the forefront of financial technology trends, appealing to tech-savvy users interested in exploring alternative investments.
Revenue Streams – Venmo Business Model Canvas

Transaction Fees: While Venmo maintains free peer-to-peer transactions for standard bank transfers and debit cards, it generates revenue by charging a 3% fee for credit card transactions; this fee structure, implemented to offset processing costs, contributes significantly to Venmo’s income while preserving its appeal of free transfers for most users.
Instant Transfer Service: Venmo offers an instant transfer option to linked bank accounts or debit cards for a 1.75% fee (minimum $0.25, maximum $25), which provides a substantial revenue stream by capitalizing on users’ desire for immediate access to funds; this service, balancing convenience with cost, has proven popular among users requiring quick liquidity.
Merchant Services: Through its “Pay with Venmo” feature, the platform charges merchants a 1.9% + $0.10 fee per transaction, generating revenue from businesses leveraging Venmo’s large user base; this strategy not only diversifies Venmo’s income sources but also strengthens its position in the e-commerce and point-of-sale markets.
Venmo Credit Card: Launched in 2020, the Venmo Credit Card provides a new revenue stream through interest charges and interchange fees; while specific revenue figures are not publicly disclosed, this addition aligns with Venmo’s strategy to expand its financial services ecosystem and capture a larger share of users’ financial activities.
Cryptocurrency Trading: Introduced in 2021, Venmo’s cryptocurrency trading feature allows users to buy, sell, and hold select cryptocurrencies, with the platform earning revenue from transaction fees; this innovative offering not only attracts crypto-enthusiasts but also positions Venmo at the forefront of digital finance trends, potentially opening up new revenue opportunities in the burgeoning crypto market.
Channels – Venmo Business Model Canvas

Mobile Application: Venmo’s primary channel is its mobile app, available on iOS and Android platforms, which serves as the core interface for users to send, receive, and manage funds; with over 90 million active users reported in 2023, the app’s intuitive design and regular updates ensure it remains the central hub for Venmo’s services.
Web Platform: While less utilized than the mobile app, Venmo’s web interface provides an alternative channel for users who prefer desktop transactions or account management; this platform, which mirrors the app’s functionality, caters to a broader user base and enhances accessibility, particularly for those managing business accounts or preferring larger screens for financial oversight.
In-Store and Online Merchant Integration: Venmo has expanded its reach by integrating with numerous merchants for in-store and online payments, allowing users to make purchases directly from their Venmo balance; this channel, which includes partnerships with over 2 million merchants, not only increases Venmo’s utility but also drives user engagement and transaction volume.
Social Media Integration: Leveraging its social feed feature, Venmo has created a unique channel that blends financial transactions with social networking; this approach, which allows users to share and comment on transactions (with privacy controls), has fostered a community-driven platform that encourages frequent engagement and viral user acquisition.
QR Code System: Venmo’s implementation of QR codes for payments and user identification serves as an innovative channel, bridging the gap between digital and physical transactions; this feature, particularly useful for in-person exchanges and small businesses, has gained traction in the post-pandemic era, offering a contactless payment solution that aligns with changing consumer preferences.
Customer Relationships – Venmo Business Model Canvas

Community-Driven Engagement: Venmo’s unique social feed feature fosters a sense of community among users, allowing them to interact through transaction notes and emoji; this approach, which turns financial transactions into social experiences, has contributed significantly to user retention and engagement, with the average user checking the app multiple times per week.
Self-Service and Automation: The platform prioritizes user autonomy through its intuitive interface and automated processes, enabling users to manage transactions, update settings, and resolve common issues independently; this self-service model, complemented by AI-powered chatbots, enhances user experience while optimizing operational efficiency.
Personalized Financial Insights: Venmo has introduced personalized spending and receiving summaries, offering users valuable insights into their financial behavior; this feature, which analyzes transaction patterns and presents data in an easily digestible format, demonstrates Venmo’s commitment to adding value beyond basic money transfer services.
Responsive Customer Support: While emphasizing self-service, Venmo maintains a multi-channel support system, including email, phone, and social media assistance; the company’s efforts to improve response times and resolution rates, particularly for security-related issues, reflect its dedication to building trust and reliability among its user base.
Educational Content and Guides: Venmo regularly produces educational content, including blog posts, video tutorials, and in-app guides, to help users navigate its features and understand financial best practices; this proactive approach to user education not only enhances the platform’s usability but also positions Venmo as a knowledgeable and trustworthy financial partner.
Key Activities – Venmo Business Model Canvas

Platform Development and Maintenance: Venmo continuously enhances its mobile app and web platform, focusing on user experience, performance, and security; this ongoing development, which includes regular updates and new feature rollouts, ensures the platform remains competitive and reliable, with the app maintaining a high 4.9-star rating on both iOS and Android app stores.
Payment Processing and Risk Management: At the core of Venmo’s operations is its sophisticated payment processing system, which handles millions of transactions daily while employing advanced fraud detection and risk management protocols; this critical activity, bolstered by machine learning algorithms, has enabled Venmo to maintain a low fraud rate of less than 0.1% of its total payment volume.
Merchant Network Expansion: Venmo actively pursues partnerships with businesses to expand its “Pay with Venmo” network, which has grown to include over 2 million merchants; this strategic activity not only diversifies Venmo’s revenue streams but also enhances its value proposition to users by offering more places to use their Venmo balance.
Data Analytics and Personalization: Leveraging its vast trove of transaction data, Venmo engages in sophisticated data analytics to derive insights for product improvements and personalized user experiences; this activity, while respecting user privacy, enables Venmo to offer tailored financial summaries and recommendations, contributing to its high user engagement rates.
Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: As a financial service provider, Venmo dedicates significant resources to ensuring compliance with evolving financial regulations and security standards; this ongoing activity, which includes regular audits and updates to privacy policies, is crucial for maintaining user trust and operational legitimacy in the highly regulated fintech sector.
Key Resources – Venmo Business Model Canvas

Technological Infrastructure: Venmo’s robust technological backbone, including its servers, databases, and cloud computing resources, forms the foundation of its operations; this infrastructure, which processes over 52 million active accounts and billions of dollars in transactions quarterly, ensures the platform’s reliability, scalability, and performance even during peak usage periods.
User Base and Network Effects: Venmo’s vast and engaged user base, surpassing 90 million active users in 2023, represents a critical resource that drives the platform’s value through network effects; this ever-growing community not only facilitates more transactions but also serves as a powerful marketing tool, with user-to-user recommendations driving organic growth.
Brand Equity and Market Position: The Venmo brand, which has become synonymous with peer-to-peer payments in the U.S., holds significant value as a key resource; this strong brand recognition, evidenced by Venmo’s consistent ranking as one of the top finance apps, enables the company to attract new users and expand into adjacent financial services with built-in trust and credibility.
Data and Analytics Capabilities: Venmo’s vast repository of transaction data, coupled with its advanced analytics capabilities, serves as a valuable resource for driving business decisions and product innovations; this data-driven approach not only enhances user experience through personalized features but also provides strategic insights for market expansion and risk management.
Strategic Partnerships: Venmo’s network of partnerships, including its integration with over 2 million merchants and collaborations with major brands, constitutes a key resource that expands its ecosystem; these strategic alliances, which include deals with companies like Uber and Grubhub, not only broaden Venmo’s utility but also create new revenue streams and strengthen its market position in the competitive fintech landscape.
Key Partners – Venmo Business Model Canvas

Financial Institutions: Venmo’s partnerships with major banks and credit card companies, including Wells Fargo, Chase, and Visa, are crucial for facilitating seamless transactions and expanding its service offerings; these collaborations not only ensure smooth fund transfers but also enable features like the Venmo Credit Card, which has seen rapid adoption since its launch in 2020.
Payment Processors and Networks: Strategic alliances with payment processors such as First Data and networks like Mastercard form the backbone of Venmo’s transaction infrastructure; these partnerships, which process millions of daily transactions, are essential for maintaining the platform’s reliability and expanding its acceptance at over 2 million U.S. merchants.
E-commerce and Service Platforms: Venmo has forged partnerships with prominent e-commerce and service platforms, including Uber, Grubhub, and Shopify, to integrate its payment system; these collaborations, which have contributed to Venmo’s total payment volume exceeding $230 billion annually, significantly enhance the platform’s utility and user engagement across various digital marketplaces.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges: In its foray into cryptocurrency, Venmo has partnered with established exchanges to offer buying, selling, and holding services for select cryptocurrencies; these partnerships, while relatively new, position Venmo at the forefront of fintech innovation and cater to the growing interest in digital currencies among its predominantly millennial and Gen Z user base.
Retail Merchants: Venmo’s expanding network of retail partners, including major brands like CVS and Foot Locker, allows users to make in-store purchases using their Venmo balance or linked payment methods; these retail partnerships, which have grown significantly since the introduction of Venmo’s QR code payment feature in 2020, are key to bridging the gap between digital and physical commerce.
Cost Structure – Venmo Business Model Canvas

Payment Processing Fees: A significant portion of Venmo’s costs stems from transaction processing fees paid to financial institutions and payment networks; these fees, which can range from 1% to 3% per transaction, are partially offset by the 3% fee Venmo charges users for credit card-funded transactions, thus maintaining a delicate balance between cost management and user affordability.
Technology Infrastructure: Venmo invests heavily in its technological backbone, including server maintenance, cloud computing services, and cybersecurity measures; while specific figures are not publicly disclosed, this cost category is crucial for ensuring the platform’s reliability and security, especially as Venmo processed over $230 billion in total payment volume in 2022.
Research and Development: To maintain its competitive edge, Venmo allocates substantial resources to R&D, focusing on feature development, user experience improvements, and innovation in areas like cryptocurrency integration; this investment, while representing a significant cost, is essential for Venmo’s long-term growth and market position in the rapidly evolving fintech landscape.
Marketing and User Acquisition: Venmo’s marketing expenses, which include digital advertising, partnerships, and promotional campaigns, form a notable part of its cost structure; although exact figures are not available, the company’s efforts to maintain its high brand awareness and attract new users in a competitive market necessitate ongoing marketing investments.
Customer Support and Fraud Prevention: As Venmo’s user base expands, so do its costs associated with customer support and fraud prevention; these operational expenses, which include maintaining support teams and implementing sophisticated fraud detection systems, are critical for preserving user trust and complying with financial regulations, despite their impact on the overall cost structure.
Summary of Venmo Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on Venmo Business Model Canvas
Venmo’s Business Model Canvas reveals a robust digital payment platform that has successfully capitalized on the peer-to-peer transaction market, particularly among younger demographics. Venmo has created a strong value proposition by leveraging its user-friendly interface, and social features, and expanding its merchant network. The company’s revenue streams are diversified through transaction fees, instant transfers, and newer offerings like cryptocurrency trading. While facing significant costs in technology and security, Venmo’s strategic partnerships and large user base contribute to its competitive advantage in the fintech industry.

This is Ahsanul Haque, someone very passionate about digital marketing, SEO, and Data Analytics and founder of the Analytics Empire and currently pursuing my major in marketing at Bangladesh University of Professionals.