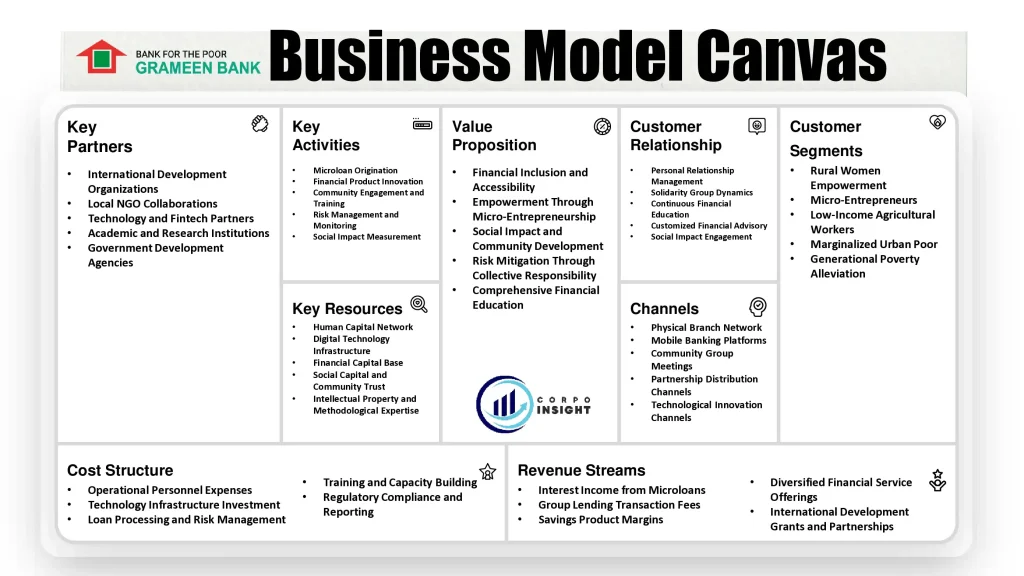
Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas 2025
Grameen Bank, pioneered by Muhammad Yunus, revolutionized microfinance by providing small, collateral-free loans to impoverished entrepreneurs, particularly women, thereby empowering marginalized communities and challenging traditional banking paradigms. In this Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas, I will identify its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting fact!
Muhammad Yunus and Grameen Bank jointly won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2006 – not the Nobel Economic Prize, which surprises many people.
Grameen Bank Competitors
BRAC | SKS Microfinance | Bandhan Bank | ASA International | FINCA International | ProCredit Holding | Kiva | Opportunity International | CARD Bank | MicroEnsure
Customer Segments – Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas

Rural Women Empowerment: Grameen Bank predominantly targets impoverished rural women, with approximately 97% of borrowers being female entrepreneurs who lack traditional banking access, thereby creating financial inclusion through microloans specifically designed for marginalized economic actors.
Micro-Entrepreneurs: The bank focuses on small-scale business owners in agricultural, handicraft, and service sectors, providing loans ranging from $50 to $500 that enable individuals to start or expand micro-enterprises without conventional collateral requirements.
Low-Income Agricultural Workers: Targeting landless farmers and agricultural laborers, Grameen Bank offers specialized agricultural microfinance products that support seasonal crop investments, livestock purchasing, and small-scale farming infrastructure development in Bangladesh’s rural regions.
Marginalized Urban Poor: Beyond rural segments, the bank extends financial services to urban slum dwellers and informal sector workers, supporting income-generating activities through group-based lending mechanisms that foster collective financial responsibility and community economic development.
Generational Poverty Alleviation: Grameen strategically segments clients who are multi-generationally impoverished, providing not just financial products but also educational support, skill development programs, and financial literacy training to break cyclical poverty patterns systematically.
Value Proposition – Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas

Financial Inclusion and Accessibility: Grameen Bank provides collateral-free microloans to unbanked populations, enabling individuals without traditional credit histories to access essential financial services and capital for entrepreneurial activities through innovative group-lending methodologies.
Empowerment Through Micro-Entrepreneurship: The bank’s value proposition centers on transforming economic potential by offering small loans that enable low-income individuals, particularly women, to initiate and expand micro-businesses, thereby generating sustainable income streams and economic mobility.
Social Impact and Community Development: Beyond financial services, Grameen creates holistic value by integrating financial products with social development initiatives, focusing on poverty alleviation, skill enhancement, and economic empowerment in marginalized rural and urban communities.
Risk Mitigation Through Collective Responsibility: The bank’s unique solidarity group model reduces lending risks by creating mutual accountability among borrowers, resulting in remarkably low default rates and sustainable financial interactions for economically vulnerable populations.
Comprehensive Financial Education: Grameen’s value extends beyond monetary transactions by providing financial literacy training, business skill development, and continuous support mechanisms that enable borrowers to make informed economic decisions and achieve long-term financial sustainability.
Revenue Streams – Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas

Interest Income from Microloans: The primary revenue stream derives from interest charges on microloans, with rates typically ranging between 15-25% annually, strategically priced to cover operational costs while remaining affordable for low-income borrowers.
Group Lending Transaction Fees: Grameen generates additional revenue through modest transaction fees associated with group lending mechanisms, leveraging collective borrowing models that reduce administrative costs and create sustainable financial interactions.
Savings Product Margins: The bank generates income by maintaining a spread between savings deposit rates and lending rates, utilizing deposited funds from members to create a self-sustaining financial ecosystem with minimal external capital requirements.
Diversified Financial Service Offerings: Beyond traditional microloans, Grameen generates revenue through complementary financial products including insurance services, pension schemes, and specialized credit programs targeting specific economic segments.
International Development Grants and Partnerships: Supplementary revenue streams emerge from strategic partnerships with international development organizations, providing additional financial resources to support microfinance operations and social impact initiatives.
Channels – Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas
Physical Branch Network: Grameen maintains an extensive network of rural branches across Bangladesh, strategically located in remote areas to provide direct, accessible financial services to marginalized communities through localized interaction points.
Mobile Banking Platforms: Leveraging digital technology, the bank has developed mobile banking applications and digital payment systems that enable remote financial transactions, expanding service accessibility for geographically dispersed microentrepreneurs.
Community Group Meetings: Utilizing a unique direct engagement channel, Grameen conducts regular group meetings where loan disbursements, repayments, and financial consultations occur collectively, fostering community-based financial interactions.
Partnership Distribution Channels: The bank collaborates with local NGOs, community organizations, and international development agencies to extend its reach, creating diversified distribution networks for financial products and services.
Technological Innovation Channels: Embracing emerging technologies, Grameen integrates digital platforms, including smartphone applications and online portals, to facilitate seamless financial interactions and expand service delivery mechanisms.
Customer Relationships – Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas

Personal Relationship Management: Grameen Bank cultivates deep, personalized relationships through regular field officer interactions, conducting weekly group meetings that provide continuous support, financial guidance, and community-based engagement beyond transactional interactions.
Solidarity Group Dynamics: The bank’s unique group lending model creates intrinsic customer relationships where borrowers mutually support and hold each other accountable, fostering strong social bonds and collective financial responsibility.
Continuous Financial Education: Beyond lending, Grameen maintains customer relationships by providing ongoing financial literacy training, skill development workshops, and entrepreneurship support mechanisms that extend customer interactions beyond monetary transactions.
Customized Financial Advisory: Bank representatives offer personalized financial counseling, tailoring loan products and repayment strategies to individual customer needs, creating adaptive and responsive relationship management approaches.
Social Impact Engagement: Grameen deepens customer relationships by integrating social development objectives, supporting borrowers’ holistic economic empowerment through targeted programs addressing health, education, and community development initiatives.
Key Activities – Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas

Microloan Origination: Grameen Bank develops and processes microloans targeting low-income entrepreneurs, utilizing innovative group-lending methodologies that assess creditworthiness through social capital and collective responsibility rather than traditional financial metrics.
Financial Product Innovation: The bank continuously designs specialized microfinance products tailored to specific economic segments, including agricultural loans, women entrepreneurship credits, and seasonal investment financing mechanisms.
Community Engagement and Training: Grameen conducts regular financial literacy workshops, skill development programs, and community-based training sessions that empower borrowers with comprehensive economic knowledge and entrepreneurial capabilities.
Risk Management and Monitoring: The bank implements sophisticated credit assessment processes, continuously monitoring loan performance, conducting field evaluations, and maintaining low default rates through proactive risk management strategies.
Social Impact Measurement: Grameen systematically tracks and analyzes the socio-economic impact of its interventions, measuring borrowers’ economic progress, community development indicators, and long-term poverty alleviation outcomes.
Key Resources – Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas

Human Capital Network: Grameen’s most critical resource comprises its extensive network of skilled field officers, community workers, and local managers who possess deep understanding of microfinance dynamics and rural economic ecosystems.
Digital Technology Infrastructure: The bank has developed robust technological platforms enabling mobile banking, digital loan processing, and real-time financial tracking systems that enhance operational efficiency and service accessibility.
Financial Capital Base: Grameen maintains a diversified financial resource base through member savings, international grants, strategic partnerships, and reinvested profits, ensuring sustainable microfinance operations without extensive external borrowing.
Social Capital and Community Trust: The bank’s intangible resource of community credibility and social networks enables effective loan disbursement, minimal default rates, and sustainable financial interactions in marginalized economic segments.
Intellectual Property and Methodological Expertise: Grameen’s proprietary group-lending model, developed over decades, represents a sophisticated intellectual resource enabling innovative approaches to financial inclusion and poverty alleviation.
Key Partners – Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas

International Development Organizations: Grameen partners with global entities like the World Bank, USAID, and UN agencies to secure funding, expertise, and strategic support for microfinance initiatives in developing economies.
Local NGO Collaborations: The bank forms strategic alliances with grassroots non-governmental organizations to extend financial services, leverage local knowledge, and enhance community-level economic empowerment programs.
Technology and Fintech Partners: Grameen collaborates with digital technology firms and fintech platforms to develop innovative mobile banking solutions, enhance digital financial infrastructure, and improve service accessibility.
Academic and Research Institutions: Strategic partnerships with universities and research centers enable continuous methodology refinement, impact assessment, and knowledge generation in microfinance and social entrepreneurship domains.
Government Development Agencies: Bilateral and multilateral government partnerships provide regulatory support, financial resources, and policy frameworks that facilitate Grameen’s expansion and social impact objectives.
Cost Structure – Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas

Operational Personnel Expenses: Field officers, branch managers, and support staff constitute the largest cost component, with extensive human resources required for localized microfinance operations and community engagement strategies.
Technology Infrastructure Investment: Significant expenses are allocated to maintaining digital platforms, mobile banking systems, and cybersecurity infrastructure that enable efficient financial transaction processing and service delivery.
Loan Processing and Risk Management: Costs associated with credit assessment, field evaluations, group meeting logistics, and sophisticated risk monitoring mechanisms represent substantial ongoing financial investments.
Training and Capacity Building: The bank invests heavily in continuous financial literacy programs, skill development workshops, and employee training initiatives that support operational effectiveness and social impact objectives.
Regulatory Compliance and Reporting: Expenses related to maintaining regulatory standards, conducting impact assessments, and generating comprehensive financial and social performance reports constitute critical organizational cost elements.
Summary of Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on Grameen Bank Business Model Canvas
Grameen Bank’s innovative business model transcends traditional banking by prioritizing social impact over pure profit. By targeting marginalized populations through group-lending methodologies, technology integration, and comprehensive financial empowerment, the bank has revolutionized microfinance, demonstrating that sustainable economic development can be achieved by providing accessible financial services to the underserved.

This is Ahsanul Haque, someone very passionate about digital marketing, SEO, and Data Analytics and founder of the Analytics Empire and currently pursuing my major in marketing at Bangladesh University of Professionals.







