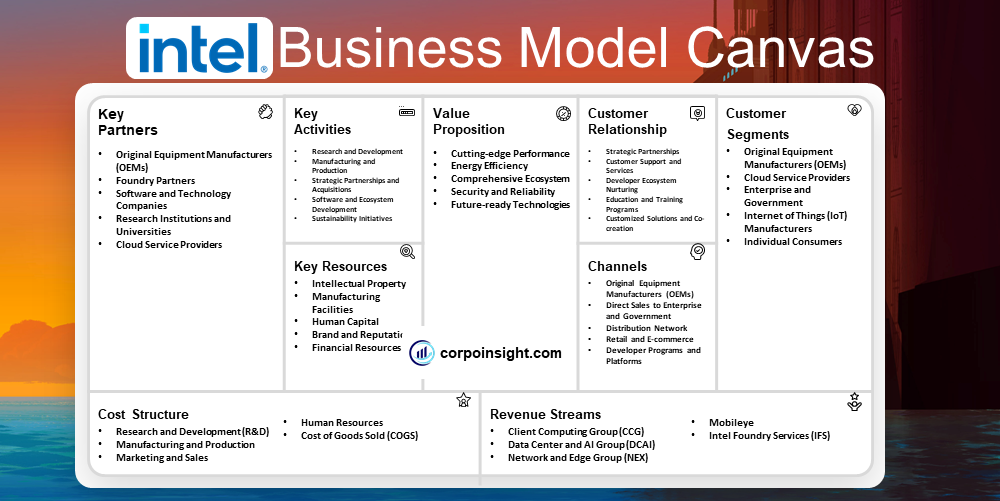
Intel Business Model Canvas 2024
Intel, the pioneering semiconductor giant that revolutionized computing with its microprocessors, continues to push the boundaries of technology despite facing fierce competition in an ever-evolving market. In this Intel Business Model Canvas, I will identify its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting fact!
The company operates its own air traffic control tower at its facility in Ronler Acres, Oregon, to manage helicopter traffic between its campuses.
Intel Competitors
Apple | AMD | NVIDIA | Samsung | Qualcomm | TSMC | IBM | Broadcom | Texas Instruments | Micron Technology
Customer Segments – Intel Business Model Canvas

Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): Intel’s primary customers include major computer manufacturers such as Dell, HP, and Lenovo, who integrate Intel processors into their devices, thereby driving a significant portion of Intel’s revenue through large-volume purchases of chips for laptops, desktops, and servers.
Cloud Service Providers: With the exponential growth of cloud computing, companies like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud have become crucial customers for Intel, purchasing high-performance processors and data center solutions to power their vast infrastructure and meet increasing demand for cloud services.
Enterprise and Government: Large corporations and government agencies form a vital segment, requiring Intel’s advanced solutions for data centers, networking, and security; these customers often seek customized solutions and long-term partnerships to address their complex computational needs and stringent security requirements.
Internet of Things (IoT) Manufacturers: As IoT continues to expand, Intel has positioned itself as a key supplier for manufacturers of smart devices, autonomous vehicles, and industrial equipment, providing specialized processors and connectivity solutions that enable the development of innovative, connected products across various sectors.
Individual Consumers: While not Intel’s primary focus, the company still caters to tech enthusiasts and DIY computer builders through its retail channels, offering high-performance processors and other components for those who seek cutting-edge technology for gaming, content creation, and other demanding applications.
Value Proposition – Intel Business Model Canvas

Cutting-edge Performance: Intel’s processors, exemplified by the latest 13th generation Core series and Xeon Scalable platforms, offer industry-leading performance for demanding applications, enabling customers to tackle complex computational tasks, from AI and machine learning to high-performance computing and advanced gaming experiences.
Energy Efficiency: Through innovations like the Intel 7 process technology and hybrid architecture in processors such as the Alder Lake series, Intel delivers a compelling balance of performance and power efficiency, addressing the growing demand for eco-friendly computing solutions in both consumer and enterprise markets.
Comprehensive Ecosystem: Intel’s value extends beyond hardware, encompassing a vast ecosystem of software tools, partnerships, and support services, including the OneAPI toolkit and Intel DevCloud, which empower developers and businesses to optimize their applications and accelerate time-to-market for innovative solutions.
Security and Reliability: With embedded security features like Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGX) and the vPro platform, Intel provides robust protection against cyber threats and ensures system stability, catering to the critical needs of enterprise customers and data-sensitive industries.
Future-ready Technologies: Intel’s investments in emerging fields such as quantum computing, neuromorphic chips, and 5G infrastructure position the company as a forward-thinking partner for businesses and researchers looking to leverage next-generation technologies and stay ahead in rapidly evolving markets.
Revenue Streams – Intel Business Model Canvas

Client Computing Group (CCG): Despite facing challenges, CCG remains Intel’s largest revenue generator, contributing $31.7 billion in 2023; this segment encompasses sales of processors and chipsets for personal computers, including both desktop and notebook platforms, catering to consumers and businesses alike.
Data Center and AI Group (DCAI): Generating $19.2 billion in 2023, DCAI focuses on providing high-performance processors, FPGAs, and specialized accelerators for data centers, cloud service providers, and enterprise customers; this segment is crucial for Intel’s growth strategy in the burgeoning AI and cloud computing markets.
Network and Edge Group (NEX): With revenue of $8.9 billion in 2023, NEX delivers solutions for network infrastructure and edge computing, including 5G technologies, ethernet solutions, and IoT products; this diverse segment positions Intel to capitalize on the expanding connectivity and edge computing trends.
Mobileye: Acquired by Intel in 2017, Mobileye contributed $1.9 billion in revenue for 2023, focusing on advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies; as automotive technology advances, this segment represents a significant growth opportunity for Intel in the rapidly evolving transportation sector.
Intel Foundry Services (IFS): Launched in 2021, IFS aims to become a major player in the semiconductor manufacturing industry, offering fab capacity to third-party customers; while still in its early stages, Intel is investing heavily in this segment to diversify its revenue streams and compete with established foundries.
Channels – Intel Business Model Canvas

Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): Intel’s most significant channel involves partnerships with major computer manufacturers such as Dell, HP, and Lenovo, who integrate Intel processors into their products; this symbiotic relationship allows Intel to reach a vast consumer base while providing OEMs with cutting-edge technology for their devices.
Direct Sales to Enterprise and Government: For large-scale clients with specific needs, Intel employs a direct sales force that works closely with enterprise and government customers to provide tailored solutions; this channel enables Intel to offer personalized support and maintain strong relationships with key accounts.
Distribution Network: Intel utilizes a global network of authorized distributors, such as Arrow Electronics and Avnet, to reach smaller OEMs, system integrators, and value-added resellers; this channel expands Intel’s market penetration and provides localized support in diverse geographical regions.
Retail and E-commerce: While not its primary focus, Intel maintains a presence in retail channels through partnerships with electronics retailers and e-commerce platforms, catering to individual consumers and small businesses; this channel includes the sale of boxed processors and other components through outlets like Best Buy and Newegg.
Developer Programs and Platforms: Intel engages with the developer community through channels like the Intel Developer Zone and Intel DevCloud, providing resources, tools, and support; this strategic approach fosters innovation, encourages the adoption of Intel technologies, and creates a loyal ecosystem of developers and partners.
Customer Relationships – Intel Business Model Canvas

Strategic Partnerships: Intel maintains deep, long-term relationships with key OEMs and cloud service providers, exemplified by its collaboration with Dell on Project Copper, which aims to develop advanced AI solutions; these partnerships often involve co-engineering efforts, ensuring Intel’s technologies align closely with customer needs and market demands.
Customer Support and Services: Through programs like Intel Customer Support and the Priority Support Professional services, Intel offers tiered support options tailored to different customer segments; this comprehensive approach includes 24/7 technical assistance, on-site support for enterprise clients, and self-service resources, ensuring customers receive appropriate care regardless of their size or needs.
Developer Ecosystem Nurturing: Intel fosters a robust developer community through initiatives like the Intel one API toolkits and Intel DevCloud, providing free resources, training, and access to cutting-edge hardware; this relationship-building strategy not only supports developers but also drives innovation and adoption of Intel technologies across various industries.
Education and Training Programs: Intel invests in customer education through platforms like Intel Partner University and Intel AI Academy, offering certifications and training programs; these initiatives help customers maximize the value of Intel products while building a skilled workforce capable of leveraging Intel’s technologies effectively.
Customized Solutions and Co-creation: For enterprise and government clients, Intel often engages in collaborative projects, such as the recent partnership with the U.S. Department of Energy on exascale computing; this co-creation approach allows Intel to develop highly specialized solutions while fostering strong, mutually beneficial relationships with key customers.
Key Activities – Intel Business Model Canvas

Research and Development: Intel invests heavily in R&D, spending $15.7 billion in 2022, focusing on areas such as advanced chip design, AI, and quantum computing; this substantial investment allows Intel to maintain its technological edge and develop groundbreaking products like its 7nm process technology and neuromorphic chips.
Manufacturing and Production: With its IDM 2.0 strategy, Intel is expanding its manufacturing capabilities, including a $20 billion investment in two new fabs in Arizona; this focus on production ensures control over the supply chain and quality while positioning Intel to offer foundry services to other companies.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions: Intel actively pursues partnerships and acquisitions to enhance its capabilities, exemplified by its recent collaboration with TSMC for chip production and the acquisition of Mobileye; these strategic moves allow Intel to access new technologies and markets rapidly.
Software and Ecosystem Development: Intel invests significantly in software development and ecosystem building, creating tools like the oneAPI platform and supporting open-source projects; this activity ensures that software is optimized for Intel hardware and fosters a community of developers and partners around Intel’s technologies.
Sustainability Initiatives: Intel is actively working towards its 2030 RISE goals, which include achieving net positive water use and 100% renewable energy; these sustainability efforts not only reduce environmental impact but also appeal to environmentally conscious customers and investors.
Key Resources – Intel Business Model Canvas

Intellectual Property: Intel’s vast portfolio of over 70,000 patents worldwide is a crucial resource, protecting its innovations in chip design, manufacturing processes, and emerging technologies; this intellectual property forms the foundation of Intel’s competitive advantage in the semiconductor industry.
Manufacturing Facilities: Intel’s network of advanced fabrication plants, including cutting-edge facilities in the US, Ireland, and Israel, represents a significant resource; these fabs, coupled with Intel’s process technology, enable the company to produce high-performance chips at scale and maintain control over its supply chain.
Human Capital: Intel’s workforce of approximately 131,900 employees (as of 2022) includes world-class engineers, researchers, and business professionals; this diverse and highly skilled talent pool drives innovation and enables Intel to tackle complex technological challenges across various domains.
Brand and Reputation: The Intel brand, recognized globally and associated with high-performance computing, is a valuable intangible resource; this strong brand reputation, built over decades, facilitates customer trust, partnerships, and market penetration across different segments.
Financial Resources: With a robust balance sheet including $43.5 billion in cash and short-term investments (as of Q4 2022), Intel has significant financial resources to fund R&D, capital expenditures, and strategic initiatives; this financial strength allows Intel to invest in long-term projects and weather market fluctuations.
Key Partners – Intel Business Model Canvas

Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): Intel maintains crucial partnerships with major computer manufacturers like Dell, HP, and Lenovo, who integrate Intel processors into their products; these symbiotic relationships not only drive Intel’s sales but also influence product development, as exemplified by the recent collaboration with Lenovo on AI-optimized workstations.
Foundry Partners: Despite being an integrated device manufacturer, Intel has formed strategic partnerships with external foundries, notably TSMC, to supplement its manufacturing capabilities; this collaboration, announced in 2021, allows Intel to leverage advanced process nodes for certain products while it works on enhancing its own manufacturing technologies.
Software and Technology Companies: Intel collaborates with numerous software giants and tech firms, such as Microsoft, Google, and SAP, to optimize their software for Intel hardware; these partnerships, like the recent expansion of Intel’s alliance with Microsoft for Windows 11 optimization, ensure seamless integration and performance across platforms.
Research Institutions and Universities: To drive innovation, Intel partners with academic institutions and research organizations worldwide; for instance, its ongoing collaboration with the Technical University of Munich on quantum computing not only advances cutting-edge technology but also helps Intel tap into emerging talent pools.
Cloud Service Providers: Intel maintains strong partnerships with major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud; these relationships, exemplified by the recent collaboration with AWS on custom chip development, are critical for Intel’s data center business and its push into AI and edge computing solutions.
Cost Structure – Intel Business Model Canvas

As a business analyst, I’ll analyze Intel’s Cost Structure based on recent data. Please note that while I aim for accuracy, it’s advisable to verify any critical information independently.
Research and Development (R&D): Intel’s substantial R&D expenditure, which reached $15.7 billion in 2022, represents a significant portion of its cost structure; this investment, crucial for maintaining technological leadership, encompasses diverse areas such as advanced chip design, AI, and quantum computing, ensuring Intel’s competitiveness in rapidly evolving markets.
Manufacturing and Production: As an integrated device manufacturer, Intel incurs substantial costs in maintaining and upgrading its fabrication facilities, with recent investments including $20 billion for new fabs in Arizona; these capital-intensive expenditures, while enabling greater control over production, also contribute significantly to Intel’s fixed cost base.
Marketing and Sales: Intel’s global marketing and sales efforts, which include initiatives like the Intel Inside program and targeted enterprise sales teams, constitute a considerable expense; while specific figures are not publicly disclosed, these costs are essential for maintaining brand awareness and driving sales across diverse market segments.
Human Resources: With a workforce of over 130,000 employees, labor costs form a substantial part of Intel’s expense structure; this includes not only salaries and benefits but also investments in training and development programs, which are crucial for attracting and retaining top talent in the competitive tech industry.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Intel’s COGS, which amounted to $38.7 billion in 2022, includes direct material costs, labor, and manufacturing overhead; while this figure fluctuates with production volumes and efficiency improvements, it remains a primary component of Intel’s cost structure, directly impacting the company’s gross margins and overall profitability.
Summary of Intel Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on Intel Business Model Canvas
Intel’s Business Model Canvas reveals a robust and complex structure built on technological leadership and strategic partnerships. The company’s focus on innovation, evidenced by substantial R&D investments, underpins its value proposition. Intel’s diverse customer segments, from OEMs to cloud providers, are served through multiple channels and supported by strong customer relationships. While facing challenges in an evolving market, Intel’s key resources, activities, and partnerships position it to adapt and maintain its significant role in the semiconductor industry.

This is Ahsanul Haque, someone very passionate about digital marketing, SEO, and Data Analytics and founder of the Analytics Empire and currently pursuing my major in marketing at Bangladesh University of Professionals.







