LinkedIn Business Model Canvas 2024
Although my career has taken me through diverse industries, from tech startups to nonprofit organizations, the common thread weaving through my professional tapestry has been an unwavering commitment to innovative problem-solving and fostering collaborative environments that drive meaningful change. In this LinkedIn Business Model Canvas, I will identify its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting fact!
The company has a tradition called “InDays” where employees get one day each month to work on personal projects or volunteer.
LinkedIn Competitors
Indeed | Glassdoor | Monster | ZipRecruiter | Xing | Upwork | Dice | CareerBuilder | AngelList | Hired
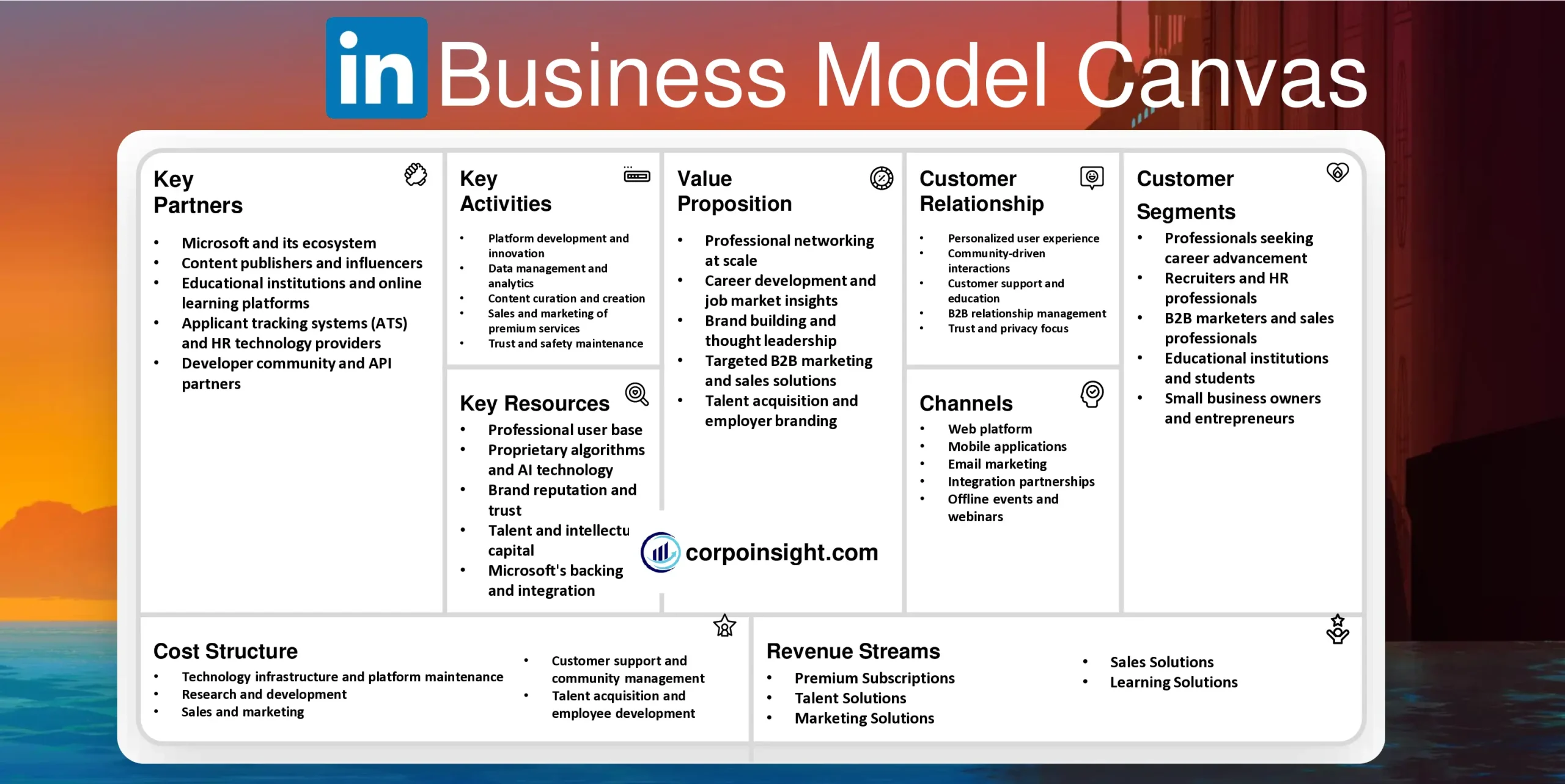
Customer Segments – LinkedIn Business Model Canvas

Professionals seeking career advancement: LinkedIn caters to a vast array of individuals, from entry-level graduates to seasoned executives, who utilize the platform to network, showcase their skills, and explore job opportunities across diverse industries and geographical locations.
Recruiters and HR professionals: This segment leverages LinkedIn’s extensive user base and sophisticated search tools to identify, engage with, and hire top talent; moreover, they use the platform to build employer branding and establish their companies as desirable workplaces.
B2B marketers and sales professionals: LinkedIn serves as a critical tool for this group, enabling them to identify decision-makers, nurture leads, and engage in targeted advertising campaigns; furthermore, they utilize the platform’s content marketing features to establish thought leadership and drive business growth.
Educational institutions and students: Universities, colleges, and other learning organizations use LinkedIn to connect with alumni, promote courses, and facilitate career services; concurrently, students leverage the platform to research potential career paths, connect with mentors, and explore internship opportunities.
Small business owners and entrepreneurs: This segment utilizes LinkedIn to build professional networks, seek potential partners or investors, and gain industry insights; additionally, they often use the platform to establish their personal brand and position themselves as experts in their respective fields.
Value Proposition – LinkedIn Business Model Canvas

Professional networking at scale: LinkedIn offers unparalleled access to a vast network of over 900 million professionals across 200 countries, enabling users to forge valuable connections, expand their professional circles, and unlock career opportunities that might otherwise remain out of reach.
Career development and job market insights: The platform provides a comprehensive suite of tools for career growth, including personalized job recommendations, skill assessments, and learning resources; furthermore, it offers real-time labor market data, empowering users to make informed decisions about their professional trajectories.
Brand building and thought leadership: LinkedIn serves as a powerful medium for individuals and companies to establish their professional brand, share industry expertise, and engage with a targeted audience; this is achieved through features like article publishing, company pages, and LinkedIn Live, which collectively foster credibility and visibility.
Targeted B2B marketing and sales solutions: With its rich user data and advanced targeting capabilities, LinkedIn offers businesses a unique platform for precision marketing; moreover, tools like Sales Navigator enable sales professionals to identify and engage with decision-makers effectively, streamlining the B2B sales process.
Talent acquisition and employer branding: LinkedIn’s robust recruitment tools, coupled with its extensive professional network, provide organizations with an efficient means to attract, evaluate, and hire top talent; additionally, the platform offers companies the opportunity to showcase their culture and values, enhancing their appeal to potential employees.
Revenue Streams – LinkedIn Business Model Canvas

Premium Subscriptions: LinkedIn offers tiered subscription plans, including Premium Career, Premium Business, Sales Navigator, and Recruiter Lite, which provide enhanced features such as advanced search filters, InMail credits, and competitive insights; these subscriptions, catering to various professional needs, contribute significantly to the platform’s recurring revenue.
Talent Solutions: This segment, which includes LinkedIn Recruiter, LinkedIn Jobs, and other hiring tools, forms the largest portion of LinkedIn’s revenue; by leveraging its vast professional network, LinkedIn provides recruiters and HR professionals with powerful tools to identify, attract, and hire top talent efficiently.
Marketing Solutions: LinkedIn’s advertising platform allows businesses to reach a highly targeted professional audience through sponsored content, sponsored InMail, and display ads; furthermore, the platform’s rich user data enables precise audience targeting, making it an attractive option for B2B marketers seeking to engage decision-makers.
Sales Solutions: Primarily driven by Sales Navigator, this revenue stream equips sales professionals with advanced lead generation and customer insight tools; by facilitating more effective B2B sales processes, LinkedIn has carved out a valuable niche in the sales enablement market.
Learning Solutions: Through LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com), the platform offers a vast library of professional development courses; this not only provides an additional revenue stream but also enhances user engagement and retention by offering valuable skill-building resources to individuals and organizations alike.
Channels – LinkedIn Business Model Canvas

Web platform: LinkedIn’s primary channel is its robust web-based platform, accessible via desktop browsers, which offers a comprehensive suite of features including profile management, networking tools, and content sharing capabilities; this central hub serves as the backbone of LinkedIn’s ecosystem, facilitating user engagement and value creation.
Mobile applications: With over 57% of LinkedIn traffic coming from mobile devices, the company has developed feature-rich iOS and Android apps that provide on-the-go access to core functionalities; these apps, which include specialized versions like LinkedIn Job Search and Sales Navigator, cater to the increasing demand for mobile-first professional networking.
Email marketing: LinkedIn leverages personalized email notifications to drive user engagement, delivering updates on network activity, job recommendations, and relevant content; this channel not only keeps users informed but also serves as a crucial touchpoint for re-engaging dormant users and promoting premium features.
Integration partnerships: LinkedIn has forged strategic integrations with various third-party platforms, including Microsoft Office 365 (following its acquisition by Microsoft), applicant tracking systems, and CRM tools; these integrations extend LinkedIn’s reach and functionality, embedding its services into users’ daily workflows and increasing platform stickiness.
Offline events and webinars: While primarily a digital platform, LinkedIn also utilizes offline channels through industry events, webinars, and LinkedIn Local meetups; these initiatives, which blend online and offline experiences, help strengthen professional communities and provide valuable networking opportunities beyond the digital realm.
Customer Relationships – LinkedIn Business Model Canvas

Personalized user experience: LinkedIn employs sophisticated algorithms to tailor content, connection suggestions, and job recommendations to each user’s profile and behavior; this personalization, which extends to features like “Your Daily Rundown” and “LinkedIn News,” enhances user engagement and perceived value, fostering a sense of individual attention at scale.
Community-driven interactions: The platform facilitates peer-to-peer relationships through features such as Groups, where professionals with shared interests can connect and collaborate; additionally, LinkedIn’s focus on user-generated content, including articles and posts, creates a self-sustaining ecosystem of professional knowledge sharing and networking.
Customer support and education: LinkedIn maintains multiple channels for customer assistance, including a comprehensive Help Center, community forums, and direct support for premium users; furthermore, the platform offers extensive educational resources, such as LinkedIn Learning courses and webinars, to help users maximize their professional growth and platform utilization.
B2B relationship management: For its corporate clients utilizing Talent, Marketing, and Sales solutions, LinkedIn provides dedicated account managers and customer success teams; these personalized relationships ensure that businesses can effectively leverage LinkedIn’s tools to achieve their objectives, whether in recruitment, marketing, or sales.
Trust and privacy focus: LinkedIn places a strong emphasis on maintaining user trust through robust privacy controls and transparent data practices; by allowing users to manage their information visibility and providing regular updates on platform policies, LinkedIn fosters a sense of security and control that is crucial for maintaining long-term user relationships in the professional networking space.
Key Activities – LinkedIn Business Model Canvas

Platform development and innovation: LinkedIn continually enhances its core platform, introducing features like Stories, Live Video, and Newsletters, while also improving existing functionalities; this ongoing innovation, which often leverages AI and machine learning, aims to increase user engagement and maintain LinkedIn’s competitive edge in the professional networking space.
Data management and analytics: The company processes vast amounts of professional data to power its recommendation engines, provide labor market insights, and enhance targeting for advertisers; moreover, LinkedIn’s Economic Graph initiative analyzes this data to generate valuable insights into global workforce trends, further solidifying its position as a leader in professional intelligence.
Content curation and creation: LinkedIn actively encourages and facilitates the creation of professional content through its publishing platform and Influencer program; additionally, the company curates and distributes relevant news and articles, positioning itself as a vital source of industry information and thought leadership.
Sales and marketing of premium services: A significant portion of LinkedIn’s activities revolves around promoting and selling its premium subscriptions and B2B solutions; this includes developing targeted marketing campaigns, providing product demonstrations, and offering customized solutions to enterprise clients, all of which contribute substantially to the company’s revenue growth.
Trust and safety maintenance: LinkedIn invests heavily in activities that preserve the integrity of its professional network, including developing advanced algorithms to detect fake profiles and spam, implementing robust privacy controls, and ensuring compliance with global data protection regulations; these efforts are crucial in maintaining user trust and the platform’s reputation as a credible professional networking site.
Key Resources – LinkedIn Business Model Canvas

Professional user base: LinkedIn’s most valuable resource is its vast network of over 900 million members across 200+ countries, representing a diverse array of industries and skill sets; this extensive professional ecosystem not only drives user engagement but also forms the foundation for LinkedIn’s various revenue streams.
Proprietary algorithms and AI technology: LinkedIn’s sophisticated algorithms, which power features like personalized content recommendations, job matching, and “People You May Know,” are critical to enhancing user experience and platform stickiness; furthermore, the company’s investments in AI and machine learning continue to drive innovations in areas such as talent matching and predictive analytics.
Brand reputation and trust: As the world’s largest professional network, LinkedIn’s brand carries significant weight in the business world; this reputation, built over two decades, allows the platform to attract new users, retain existing ones, and command premium prices for its services, while also facilitating partnerships with other industry leaders.
Talent and intellectual capital: LinkedIn’s workforce, comprising skilled professionals in technology, data science, sales, and customer success, is crucial to its continued innovation and growth; moreover, the company’s culture of innovation, fostered through initiatives like InDays, contributes to its ability to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Microsoft’s backing and integration: Since its acquisition by Microsoft in 2016, LinkedIn has gained access to additional resources, technologies, and integration opportunities; this symbiotic relationship has enabled LinkedIn to enhance its offerings, such as integrating with Microsoft 365 products, while also expanding its reach within the enterprise market.
Key Partners – LinkedIn Business Model Canvas

Microsoft and its ecosystem: Following Microsoft’s acquisition, LinkedIn has forged deep integrations with various Microsoft products, such as Office 365, Dynamics CRM, and Azure; this strategic partnership not only enhances LinkedIn’s offerings but also expands its reach into enterprise markets, creating a powerful synergy between professional networking and productivity tools.
Content publishers and influencers: LinkedIn collaborates with major media outlets, industry thought leaders, and content creators to populate its platform with high-quality, professional content; these partnerships, which include initiatives like the LinkedIn Influencer program, help maintain user engagement and position LinkedIn as a go-to source for professional insights and news.
Educational institutions and online learning platforms: To bolster its Learning Solutions, LinkedIn partners with universities, professional associations, and e-learning providers to offer a diverse range of courses and certifications; these collaborations, which include integrations with platforms like Coursera and edX, enhance LinkedIn’s value proposition in professional development and lifelong learning.
Applicant tracking systems (ATS) and HR technology providers: LinkedIn maintains integrations with numerous ATS and HR platforms, such as Workday, Oracle, and SAP SuccessFactors; these partnerships streamline recruitment processes for employers, enhancing the effectiveness of LinkedIn’s Talent Solutions while also increasing the platform’s stickiness in corporate HR ecosystems.
Developer community and API partners: Through its Developer Program and API offerings, LinkedIn cultivates a network of third-party developers and technology partners who create applications and integrations that extend the platform’s functionality; this ecosystem of partners helps LinkedIn reach new markets, enhance user experiences, and drive innovation beyond its core offerings.
Cost Structure – LinkedIn Business Model Canvas

Technology infrastructure and platform maintenance: As a large-scale digital platform, LinkedIn incurs significant costs related to server infrastructure, data storage, and software development; these ongoing expenses are essential for ensuring the stability, security, and continuous improvement of the platform to meet the evolving needs of its growing user base.
Research and development: LinkedIn invests heavily in research and development, dedicating resources to developing new features, enhancing user experiences, and exploring innovative technologies; this commitment to innovation is crucial for maintaining LinkedIn’s competitive edge, driving user engagement, and expanding its service offerings to both individual and enterprise customers.
Sales and marketing: To acquire new users, promote premium subscriptions, and market its B2B solutions, LinkedIn allocates substantial resources to sales and marketing activities, including digital advertising, content creation, events, and the maintenance of a global sales force; these costs are essential for driving user growth and revenue generation.
Customer support and community management: LinkedIn devotes resources to providing comprehensive customer support, managing user communities, and moderating platform content; these investments help ensure a positive user experience, address customer concerns, and maintain the integrity of the professional network, all of which contribute to user retention and loyalty.
Talent acquisition and employee development: As a knowledge-intensive business, LinkedIn’s most significant cost is its workforce, which includes skilled engineers, data scientists, product managers, and customer success professionals; the company invests in attracting, retaining, and developing top talent to drive innovation, deliver excellent customer service, and execute its strategic objectives.
Summary of LinkedIn Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on LinkedIn Business Model Canvas
In summary, LinkedIn’s robust business model is underpinned by its vast professional network, innovative technology, and diversified revenue streams. By catering to the needs of individual users, recruiters, marketers, and sales professionals, LinkedIn has established itself as the preeminent platform for career advancement and talent acquisition. Leveraging strategic partnerships, data-driven insights, and a focus on trust and user experience, LinkedIn continues to solidify its position as a dominant force in the digital professional networking landscape, poised for sustained growth and evolution.

Majoring in marketing from Bangladesh University of Professionals, Sadman Abrar is a learner, obsessed with branding and intrigued to learn about different company strategies, and currently working at bKash.