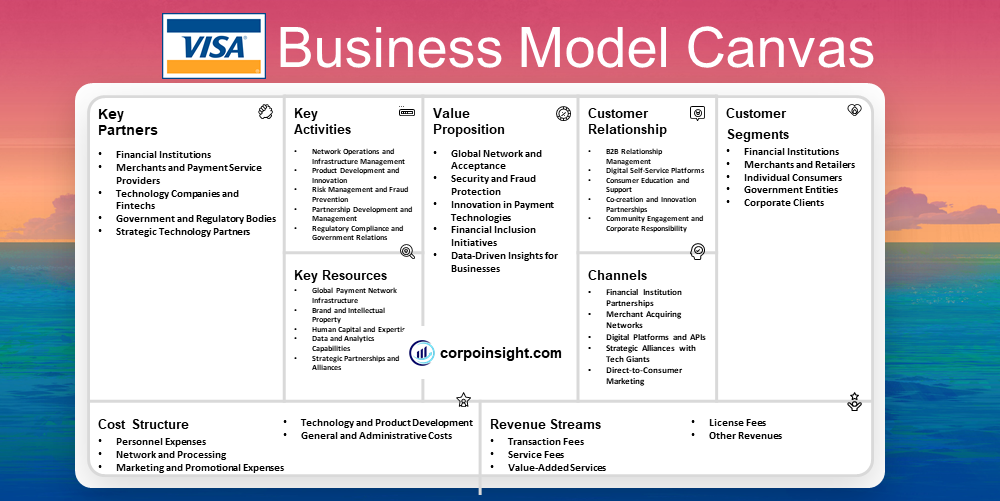
Visa Business Model Canvas 2024
While Visa began as a simple credit card program in the 1950s, it has evolved into a global powerhouse that facilitates trillions of dollars in transactions annually, connecting consumers, businesses, and financial institutions across more than 200 countries and territories. In this Visa business model canvas, we will learn its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting fact!
Visa’s data centers process an average of 1,700 transactions per second, and they’re capable of handling more than 65,000 transaction messages per second.
Visa Competitors
Mastercard | American Express | Discover | PayPal | UnionPay | JCB | Stripe | Square | Adyen | Worldpay
Customer Segments – Visa Business Model Canvas

Financial Institutions: Visa partners with banks, credit unions, and fintech companies, enabling them to issue Visa-branded cards and access its payment network. For instance, major issuers like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America offer a wide range of Visa cards to their customers.
Merchants and Retailers: Businesses of all sizes, from multinational corporations to small local shops, constitute a crucial segment for Visa. The company provides payment processing solutions, helping merchants like Amazon, Walmart, and millions of smaller businesses to accept electronic payments securely and efficiently.
Individual Consumers: Visa serves billions of cardholders worldwide, offering various products such as credit, debit, and prepaid cards. As of 2023, Visa reported over 4.2 billion cards in circulation globally, catering to diverse consumer needs and preferences across different demographics and regions.
Government Entities: Visa collaborates with governmental bodies to facilitate electronic payments for public services, social benefits, and tax collections. For example, the U.S. Treasury uses Visa’s network for certain federal payment programs, streamlining financial transactions between citizens and the government.
Corporate Clients: Visa provides specialized services for large corporations, including commercial cards, virtual cards, and expense management solutions. Companies like IBM and General Electric utilize Visa’s corporate payment solutions to optimize their financial operations and manage employee expenses more effectively.
Value Proposition – Visa Business Model Canvas

Global Network and Acceptance: Visa’s extensive network, spanning over 200 countries and territories, offers unparalleled convenience and accessibility for cardholders. With more than 80 million merchant locations accepting Visa globally, consumers can confidently use their cards for transactions virtually anywhere, from high-street retailers to online marketplaces.
Security and Fraud Protection: Leveraging advanced technologies like AI and machine learning, Visa provides robust security measures that processed 453 billion transactions in 2022 while preventing an estimated $27 billion in fraud. This commitment to security instills trust in both consumers and merchants, ensuring safe and reliable transactions.
Innovation in Payment Technologies: Visa continually pioneers new payment solutions, such as contactless payments and digital wallets, to meet evolving consumer preferences. For instance, Visa Token Service, which replaces sensitive account information with unique digital identifiers, has tokenized over 2.5 billion cards as of 2023, enhancing security for digital transactions.
Financial Inclusion Initiatives: Through programs like Visa Direct and partnerships with fintech companies, Visa extends financial services to underserved populations worldwide. By 2023, Visa had helped bring 500 million previously unbanked individuals into the formal financial system, contributing to global economic development and financial literacy.
Data-Driven Insights for Businesses: Visa’s analytics capabilities provide valuable insights to merchants and financial institutions, helping them make informed decisions. For example, Visa Consulting & Analytics offers tailored solutions that have helped clients achieve up to 7% improvement in portfolio performance and a 3-5% reduction in fraud rates.
Revenue Streams – Visa Business Model Canvas

Transaction Fees: Visa generates a significant portion of its revenue through transaction fees, which are charged each time a Visa card is used. In fiscal year 2023, these fees, including data processing and international transaction fees, accounted for approximately 70% of Visa’s net revenue, amounting to $20.8 billion.
Service Fees: Visa charges financial institutions service fees based on the payment volume of their Visa-branded cards. This revenue stream, which is calculated quarterly, contributed about 20% to Visa’s net revenue in 2023, totalling $5.9 billion and reflecting the company’s role in facilitating global payment services.
Value-Added Services: Offering a suite of products beyond basic payment processing, such as fraud prevention, analytics, and advisory services, Visa has expanded its value-added services revenue. This segment grew by 20% in 2023, reaching $6.1 billion, demonstrating Visa’s successful diversification strategy and ability to meet evolving client needs.
License Fees: Visa collects license fees from financial institutions for the right to use its brand and technology. While not as substantial as other streams, these fees, which are often negotiated based on card issuance volume and other factors, contribute to Visa’s overall revenue and help maintain its global brand presence.
Other Revenues: Visa generates additional income through various smaller revenue streams, including fees for currency conversion services and digital solutions. Although these constitute a smaller percentage of total revenue, they represent Visa’s ongoing efforts to innovate and capture value across the payments ecosystem.
Channels – Visa Business Model Canvas

Financial Institution Partnerships: Visa’s primary channel involves collaborating with banks and credit unions, which issue Visa-branded cards to consumers and businesses. In 2023, Visa partnered with over 15,000 financial institutions globally, leveraging these relationships to distribute its products and services to millions of cardholders worldwide.
Merchant Acquiring Networks: Through partnerships with merchant acquirers and payment processors, Visa extends its reach to millions of merchants. By 2023, Visa’s network encompassed over 100 million merchant locations globally, facilitating seamless transactions and providing value-added services to businesses of all sizes.
Digital Platforms and APIs: Visa’s Developer Platform and open APIs enable fintech companies and developers to integrate Visa’s payment capabilities into their applications. With over 1,000 fintech partners utilizing these tools by 2023, Visa has significantly expanded its digital distribution channels and fostered innovation in the payment ecosystem.
Strategic Alliances with Tech Giants: Collaborations with major technology companies like Apple, Google, and Samsung have allowed Visa to integrate its services into popular digital wallets and mobile payment solutions. These partnerships, which reached over 50 by 2023, have been crucial in adapting to changing consumer preferences and expanding Visa’s digital presence.
Direct-to-Consumer Marketing: While Visa primarily operates through B2B channels, it also engages in direct-to-consumer marketing to build brand awareness and preference. Through global sponsorships, such as the Olympics and FIFA World Cup, and targeted digital campaigns, Visa reached an estimated 3 billion consumers in 2023, influencing card choice and usage.
Customer Relationships – Visa Business Model Canvas

B2B Relationship Management: Visa maintains dedicated account management teams for its financial institution clients and large merchants, providing personalized support and strategic guidance. In 2023, Visa reported a client retention rate of over 95%, demonstrating the strength of these relationships and the value they deliver to partners.
Digital Self-Service Platforms: Through the Visa Online portal and mobile apps, Visa offers self-service tools for clients to manage accounts, access reports, and utilize various services. By 2023, over 90% of Visa’s institutional clients were actively using these digital platforms, streamlining interactions and improving operational efficiency.
Consumer Education and Support: Visa invests in financial literacy programs and consumer education initiatives, fostering trust and loyalty among cardholders. The Practical Money Skills program, for instance, reached over 100 million people globally in 2023, helping consumers make informed financial decisions while strengthening Visa’s brand reputation.
Co-creation and Innovation Partnerships: Visa collaborates with clients and partners to co-create innovative payment solutions, fostering deeper relationships. The Visa Innovation Centers, present in 10 global locations by 2023, have facilitated over 5,000 client engagements, driving joint innovation and strengthening Visa’s position as a trusted technology partner.
Community Engagement and Corporate Responsibility: Through initiatives like the Visa Foundation and local community programs, Visa builds relationships beyond its core business. In 2023, Visa committed $200 million to support small and micro businesses, particularly those owned by women, enhancing its reputation and fostering goodwill among diverse stakeholders.
Key Activities – Visa Business Model Canvas

Network Operations and Infrastructure Management: Visa’s core activity involves maintaining and expanding its global payment network, which processed over 193 billion transactions in 2023. This includes continuous investment in data centers, cybersecurity, and network capacity to ensure 99.999% system availability, even during peak periods like holiday shopping seasons.
Product Development and Innovation: Visa consistently develops new payment technologies and services to stay competitive. In 2023, Visa introduced Visa+, a platform enabling account-to-account payments, and expanded Visa Direct capabilities, processing 5.9 billion transactions, showcasing the company’s commitment to innovation in real-time payments and digital solutions.
Risk Management and Fraud Prevention: Leveraging advanced AI and machine learning, Visa’s risk management activities are crucial for maintaining trust in its network. In 2023, Visa’s AI-powered risk-scoring engine analyzed 100% of transactions in real time, preventing an estimated $30 billion in fraud, thereby safeguarding consumers and merchants alike.
Partnership Development and Management: Visa actively cultivates and manages partnerships with financial institutions, merchants, and technology companies. By 2023, Visa had established over 100 strategic partnerships with fintech companies and collaborated with 15,000+ financial institutions globally, expanding its ecosystem and driving innovation in digital payments.
Regulatory Compliance and Government Relations: Given the financial industry’s heavily regulated nature, Visa dedicates significant resources to ensuring compliance and shaping policy. In 2023, Visa engaged with regulators in over 200 countries, participating in key discussions on topics such as open banking, cryptocurrency regulations, and data privacy, to navigate the complex global regulatory landscape.
Key Resources – Visa Business Model Canvas

Global Payment Network Infrastructure: Visa’s VisaNet, capable of handling over 65,000 transaction messages per second, forms the backbone of its operations. This robust network, which processed 255 billion transactions in 2023, relies on state-of-the-art data centers and over 10 million miles of fibre optic cable, ensuring unparalleled speed and reliability.
Brand and Intellectual Property: Visa’s brand, valued at $49.1 billion in 2023 by Interbrand, is a critical asset that engenders trust and recognition worldwide. The company’s extensive portfolio of over 5,000 patents, covering technologies from blockchain to biometrics, underscores its innovation leadership and protects its competitive edge in the payments industry.
Human Capital and Expertise: With a workforce of approximately 26,500 employees as of 2023, Visa’s human resources, particularly in technology and data science, are crucial. The company’s talent pool, which includes over 10,000 technology professionals, drives innovation and maintains Visa’s technological supremacy in the rapidly evolving fintech landscape.
Data and Analytics Capabilities: Visa’s vast data repository, encompassing billions of transactions, coupled with advanced analytics and AI capabilities, provides invaluable insights. This resource not only enhances fraud detection but also enables Visa to offer data-driven services to clients, processing over 12 billion AI-driven decisions daily in 2023.
Strategic Partnerships and Alliances: Visa’s extensive network of partnerships, including collaborations with over 15,000 financial institutions and 100 million merchant locations globally, constitutes a key resource. These relationships, nurtured over decades, provide Visa with unparalleled market access and collaborative innovation opportunities, reinforcing its market position.
Key Partners – Visa Business Model Canvas

Financial Institutions: Visa’s partnerships with banks and credit unions form the cornerstone of its business model, with over 15,000 financial institution partners globally as of 2023. These collaborations, which include major players like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America, enable Visa to reach billions of consumers and businesses through co-branded card issuance and payment services.
Merchants and Payment Service Providers: Visa’s network of merchants, spanning over 100 million locations worldwide, is vital for transaction processing and acceptance. Strategic partnerships with global retailers like Amazon and Walmart, alongside collaborations with payment service providers such as Square and Stripe, ensure widespread acceptance of Visa payments across diverse commercial environments.
Technology Companies and Fintechs: Collaborations with tech giants and innovative fintechs drive Visa’s digital transformation and expansion. By 2023, Visa had established partnerships with over 1,000 fintech companies globally, including notable alliances with Apple (for Apple Pay), Google (for Google Pay), and emerging players like Revolut and N26, fostering innovation in digital payments and financial services.
Government and Regulatory Bodies: Visa maintains crucial partnerships with governmental organizations and regulatory authorities across its operating markets. These relationships, which span over 200 countries and territories, are essential for ensuring compliance, shaping favorable policy environments, and participating in initiatives like the development of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs).
Strategic Technology Partners: Visa collaborates with leading technology providers to enhance its infrastructure and service offerings. Partnerships with companies like IBM for blockchain solutions, Amazon Web Services for cloud computing, and cybersecurity firms like FireEye bolster Visa’s technological capabilities, ensuring the company remains at the forefront of payment innovation and security.
Cost Structure – Visa Business Model Canvas

Personnel Expenses: As a technology-driven company, Visa’s largest cost component is its workforce, with personnel expenses reaching $5.4 billion in fiscal year 2023. This investment in human capital, which includes salaries, benefits, and stock-based compensation for over 26,500 employees globally, is crucial for maintaining Visa’s innovation edge and operational excellence.
Network and Processing: Visa’s robust global payment network requires significant ongoing investment, with network and processing costs totalling $864 million in 2023. This expenditure, which encompasses data center operations, network maintenance, and cybersecurity measures, ensures the reliability and security of Visa’s infrastructure which processes billions of transactions annually.
Marketing and Promotional Expenses: To maintain brand visibility and drive card usage, Visa invested $1.1 billion in marketing and promotional activities in 2023. This substantial outlay, which includes global sponsorships like the Olympics and FIFA World Cup, as well as targeted digital campaigns, is essential for reinforcing Visa’s market position and driving transaction volume growth.
Technology and Product Development: Visa’s commitment to innovation is reflected in its technology and product development expenses, which amounted to $1.4 billion in 2023. This investment, covering areas such as AI, blockchain, and new payment solutions, is vital for Visa’s long-term competitiveness and ability to meet evolving consumer and merchant needs in the digital economy.
General and Administrative Costs: Visa incurred $1.3 billion in general and administrative expenses in 2023, encompassing costs related to legal services, consulting, facilities management, and corporate functions. While less directly tied to revenue generation, these expenditures are crucial for maintaining Visa’s global operations, ensuring regulatory compliance, and supporting overall business strategy execution.
Summary of Visa Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on Visa Business Model Canvas
Visa’s business model canvas reveals a robust ecosystem built on a global payment network, leveraging strong partnerships with financial institutions and merchants. Its value proposition centers on secure, efficient transactions and innovative payment solutions. Key revenue streams from transaction fees and value-added services support ongoing investments in technology and security. Visa’s success hinges on balancing technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and strategic partnerships while maintaining consumer trust in an increasingly digital financial landscape.

Majoring in marketing from Bangladesh University of Professionals, Sadman Abrar is a learner, obsessed with branding and intrigued to learn about different company strategies, and currently working at bKash.






