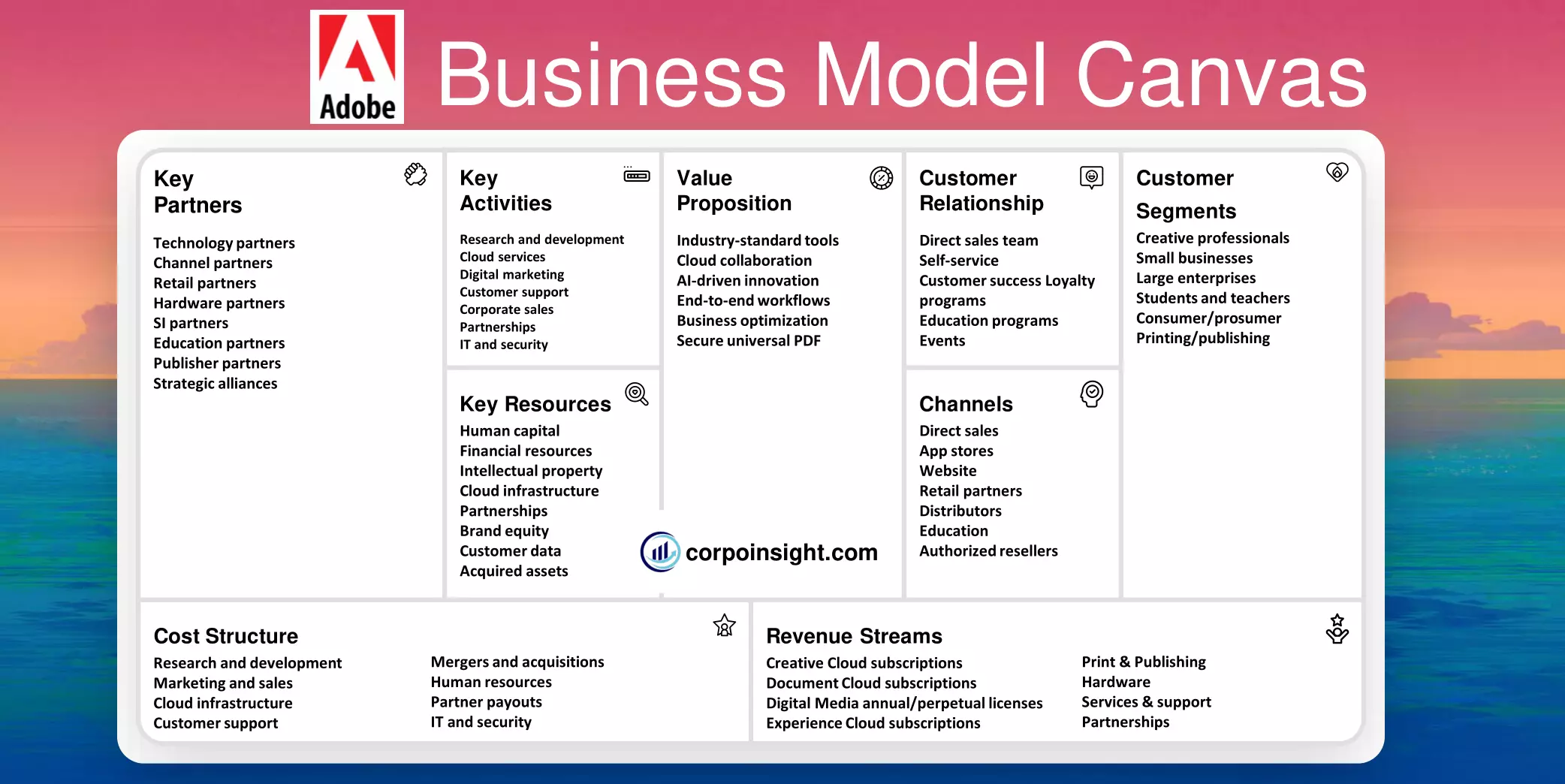
Adobe Business Model Canvas 2024
Adobe has built itself a $283.82B company in four decades, providing millions of users with diverse offerings, and in this Adobe Business Model Canvas, we will learn its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting fact!
The Adobe Acrobat Reader app icon is a stylized Acrobat Acrobat, but it started as a paper clip named Clipper.
Adobe Competitors
Corel | Autodesk | Apple | Microsoft | Wacom | Canva | Affinity | Blender | GIMP | Pixlr
Customer Segments – Adobe Business Model Canvas

Creative professionals: Adobe targets creative professionals like graphic designers, web developers, photographers, videographers, and animators. Products like Photoshop, Illustrator, and Premiere Pro are staples for these users. Adobe has over 20 million paid Creative Cloud subscribers as of 2022.
Small businesses: Small companies rely on Adobe for graphic design, marketing, and web content creation tools. The Acrobat product line aids small business workflow. Over 40% of Adobe’s Creative Cloud subscribers come from small and mid-sized businesses.
Large enterprises: Adobe sells Creative Cloud and Document Cloud enterprise licenses to large companies. Over 90% of Fortune 100 companies use Adobe Sign for secure digital documents and workflows. Major brands depend on Adobe analytics and campaign optimization.
Students and teachers: Adobe offers discounted pricing for Creative Cloud to students and teachers. This exposes new users to Adobe products while studying design, photography, etc. Over 2,000 institutions globally use Adobe Curriculum to teach digital media skills.
Consumer/prosumer: Average consumers use free or low-cost Adobe apps like Photoshop Express, Acrobat Reader, and Adobe Spark. Adobe strategically targets prosumers to upgrade them to paid versions over time as their skills improve.
Printing/publishing: Adobe aims to specialize products in the printing, publishing, and newspaper industries. Server-based PostScript and OPI improve publishing workflows. Major magazines and newspapers use Adobe to produce digital and print content.
Value Proposition – Adobe Business Model Canvas

Industry-standard tools: Adobe offers many of the foremost creative software tools like Photoshop, Premiere Pro, Illustrator, and InDesign. This gives professionals access to premium tools used industry-wide. Over 90% of creative professionals use Adobe apps.
Cloud collaboration: Creative Cloud enables seamless collaboration and cloud storage for work. Teams can share files and libraries to work together. Adobe has over 20 million Creative Cloud subscribers collaborating through the cloud.
AI-driven innovation: Adobe Sensei AI powers automated features like one-click background removal in Photoshop. This helps creatives work faster and saves time. Over 80% of large companies use Adobe’s AI services.
End-to-end workflows: Products integrate across Adobe’s clouds, allowing end-to-end workflows. A photographer can go from Lightroom to Photoshop to Spark in one ecosystem. Adobe aims to be a one-stop shop.
Business optimization: Adobe Analytics provides data insights to optimize business operations and campaigns. Companies improve customer experience and ROI. The Adobe Experience Cloud generates over $1 billion in annual revenue.
Secure universal PDF: Adobe invented the PDF format that is universally used to share and print documents securely. Features like redaction and signing are crucial for businesses. Over 2 billion PDFs are opened via Adobe Acrobat per year.
Revenue Streams – Adobe Business Model Canvas

Creative Cloud subscriptions: Creative Cloud is Adobe’s software subscription service for creative apps like Photoshop and Premiere Pro. Creative Cloud subscriptions accounted for $7.16 billion in revenue in 2022.
Document Cloud subscriptions: Document Cloud offers subscriptions for Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Sign products for PDF services. It generated $1.69 billion in subscription revenue in 2022.
Digital Media annual/perpetual licenses: Adobe still sells some perpetual licenses for certain products like Lightroom. Digital Media licensing brought in $443 million in revenue in 2022.
Experience Cloud subscriptions: Experience Cloud tools for marketing, analytics, advertising, etc., pulled in $4.01 billion in subscription revenue in 2022 as Adobe pivots to SaaS.
Print & Publishing: Adobe’s Print & Publishing segment targets the printing, newspaper, and publishing industries. This segment accounted for $148 million in revenue in 2022.
Hardware: Adobe sells specialty displays like the Adobe Broadcast Monitor for video production professionals, generating minor revenue.
Services & Support: Training, consulting, and customer support services for Adobe products made up $732 million in 2022 revenue.
Partnerships: Adobe forms partnerships with companies to integrate Adobe technologies, which contributes some licensing revenue. An example is the Microsoft OneDrive partnership.
Channels – Adobe Business Model Canvas

Direct sales: Adobe sells directly to enterprise customers for large-scale deployments of Creative Cloud and Document Cloud. Nearly 40% of Adobe’s revenue comes through direct enterprise sales teams.
App stores: Adobe distributes consumer and professional apps on the Apple App Store and Google Play Store. Many starter Adobe apps like Photoshop Express are free on app stores to gain adoption.
Website: Customers can purchase and manage subscriptions directly through Adobe’s website. Adobe.com also provides product information, tutorials, and community forums.
Retail partners: Adobe partners with electronics and office supply retailers to sell boxed software to consumers globally. Some perpetual licenses are only available through retail channels.
Distributors: Adobe leverages IT distributors like Ingram Micro to resell licenses to managed service providers and small app developers. Distributors expanded Adobe’s global reach.
Education: Adobe markets discounted education pricing to schools and universities directly. This exposes future creatives to Adobe tools while learning design and photography.
Authorized resellers: Large authorized resellers like CDW and Insight help deliver Adobe products to small and mid-sized business customers. Resellers account for around 30% of revenue.
Customer Relationships – Adobe Business Model Canvas

Direct sales team: Adobe builds long-term relationships with enterprise customers via a dedicated sales team for personalized service and account management. Nearly 40% of revenue comes from large accounts.
Self-service: Users can access tutorials, knowledge bases, community forums, and more through Adobe.com for self-help. These scales support Adobe’s broad consumer base.
Customer success managers: Adobe provides customer success managers for their top enterprise accounts to drive adoption and maximize ROI from Adobe tools. This ensures strong retention.
Loyalty programs: Adobe offers loyalty benefits like exclusive training content and priority support levels for long-term Creative Cloud subscribers. This incentivizes renewal and upsells.
Education programs: Adobe fosters relationships with the creative community by offering discounted software and curriculum resources to schools and students. This cultivates future loyalty.
Events: Adobe hosts the annual Adobe Summit event and other localized events to connect with customers and showcase new innovations. This builds brand loyalty.
Social media: Adobe engages customers and responds to issues on social media channels like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. This facilitates real-time customer service at scale.
Key Activities – Adobe Business Model Canvas

Research and development: Adobe invests heavily in R&D to pioneer new creative tools and technologies like Adobe Sensei AI. In 2022, Adobe spent over $2 billion on R&D.
Cloud services: Adobe operates enterprise cloud infrastructure and services to deliver its Creative Cloud, Document Cloud, and Experience Cloud offerings to users globally. Adobe has over 30 data centers worldwide.
Digital marketing: Adobe applies its own marketing analytics tools to optimize marketing campaigns across search, social, email, and more to attract new customers. Adobe spends over $700 million annually on S&M.
Customer support: Adobe provides multi-channel technical support and services for its broad enterprise and consumer customer base across verticals. Support staff assists with onboarding and training.
Corporate sales: Adobe has dedicated sales teams that develop customized solutions and licensing packages optimized for each enterprise customer’s needs and use cases.
Partnerships: Adobe forms strategic partnerships with companies like Microsoft, Apple, and Amazon Web Services to integrate Adobe tools and services with other platforms.
IT and security: Adobe prioritizes IT operations and cybersecurity to ensure platform stability and prevent vulnerabilities. This is crucial for customers using cloud-based services.
Mergers and acquisitions: Adobe acquires companies to obtain new technologies and talent. Recent acquisitions include Figma, Frame.io, and Allegorithmic.
Key Resources – Adobe Business Model Canvas

Human capital: Adobe employs over 28,000 people globally, including world-class engineers, designers, IT professionals, and creative experts. Its talent drives innovation.
Financial resources: With annual revenues of $17.6 billion and profit margins above 30%, Adobe has substantial financial capital to invest in growth initiatives.
Intellectual property: Adobe’s patents, trademarks, and proprietary technology around Photoshop, PDF, digital imaging, etc. provide a competitive advantage. Adobe has over 13,000 patents.
Cloud infrastructure: Adobe utilizes AWS cloud computing and has 30+ proprietary data centers globally to deliver its cloud-based Creative, Document, and Experience services.
Partnerships: Key partnerships with companies like Microsoft, Apple, and enterprise resellers expand Adobe’s distribution and integrate its technology.
Brand equity: Adobe’s brand and reputation for creative software gives it pricing power and a loyal customer base to upsell services. Brand value is estimated at $16 billion.
Customer data: With insights into how creatives work, Adobe leverages customer usage data to improve products and develop new features using AI/ML technology.
Acquired assets: Adobe obtains valuable technology, IP, and talent through strategic mergers and acquisitions. Recent examples include Figma and Frame.io.
Key Partners – Adobe Business Model Canvas

Technology partners: Adobe partners with Microsoft, Apple, Meta, and Amazon Web Services to integrate its tools with platforms like Windows, macOS, Oculus, and AWS Cloud.
Channel partners: Resellers like Ingram Micro and CDW provide licensing, training, and support for Adobe products to their business customers. They expand Adobe’s reach.
Retail partners: Retailers like Best Buy and Amazon act as sales channels to sell Adobe consumer software. In-store displays and promotions boost awareness.
Hardware partners: Adobe partners with device makers Wacom, NVIDIA, and AMD to optimize Adobe apps for pen, touch, and graphics hardware. This improves user experience.
SI partners: Systems integrators like Accenture, Deloitte, and Cognizant develop custom solutions for enterprises using Adobe’s platform and services.
Education partners: Adobe partners with schools and universities to provide curriculum resources and discounts on software. This cultivates skilled future talent.
Publisher partners: Key partnerships with magazine and newspaper publishers monetize publishing tools. Adobe works with leading media brands.
Strategic alliances: Adobe maintains partnerships with companies like Workfront, Microsoft, and ServiceNow to enable workflow integrations between platforms.
Cost Structure – Adobe Business Model Canvas

Research and development: Adobe invested over $2 billion in R&D in 2022, comprising around 12% of revenue. This reflects high costs for continuous product innovation.
Marketing and sales: Adobe spends over $2 billion annually on sales, marketing, and G&A, including large sales teams and customer acquisition costs. This is around 11% of revenue.
Cloud infrastructure: Operating 30+ proprietary data centers globally for Adobe’s cloud services requires high capital expenditure and ongoing costs.
Customer support: Providing multi-channel technical support and training to customers across verticals generates substantial staffing and support costs.
Mergers and acquisitions: Adobe routinely acquires companies and technologies, with deals like Figma costing over $20 billion. These drive growth but increase costs.
Human resources: Adobe’s over 28,000 employees in R&D, creative fields, marketing, IT, and more result in sizable recurring HR costs.
Partner payouts: Adobe shares recurring subscription revenue with resellers and other channel partners under profit-sharing agreements.
IT and security: Adobe dedicates resources to cybersecurity, compliance, and maintaining a robust IT infrastructure for its services.
Summary of Adobe Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on Adobe Business Model Canvas
Adobe has built an extremely successful business model by providing industry-leading creative software and services to customers across multiple segments. Through continual innovation, strategic partnerships, and subscription-based SaaS offerings like Creative Cloud, Adobe delivers tremendous value to creatives, businesses, and consumers worldwide. The company has established a diverse global revenue stream and maintains its competitive edge by investing heavily in R&D as well as sales, marketing, and customer support.

Majoring in marketing from Bangladesh University of Professionals, Sadman Abrar is a learner, obsessed with branding and intrigued to learn about different company strategies, and currently working at bKash.







