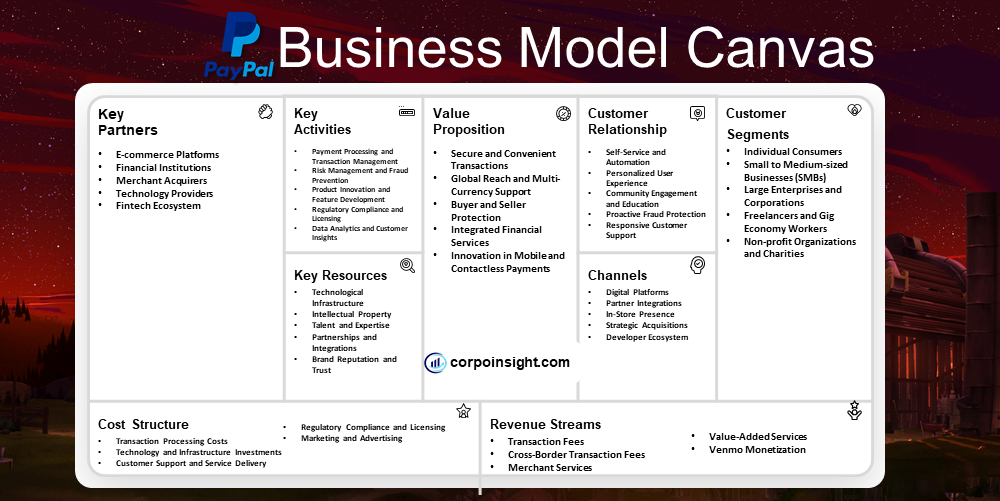
Paypal Business Model Canvas 2024
PayPal, which revolutionized online payments and paved the way for digital financial transactions, has become an indispensable tool for millions of users worldwide, enabling seamless monetary exchanges across borders and platforms. In this Paypal Business Model Canvas, we will identify its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting fact!
Before settling on the name PayPal, the company briefly considered calling itself “X.com” after merging with Elon Musk’s online banking company.
Paypal Competitors
Stripe | Square | Apple Pay | Google Pay | Venmo | TransferWise (now Wise) | Skrill | Payoneer | Adyen | Authorize.Net
Customer Segments – Paypal Business Model Canvas

Individual Consumers: PayPal caters to a vast array of individual users who rely on the platform for peer-to-peer transfers, online shopping, and digital wallet services. This segment includes tech-savvy millennials, who appreciate the convenience of mobile payments, as well as older generations adapting to digital finance solutions.
Small to Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs): A significant portion of PayPal’s customer base comprises SMBs that leverage the platform’s payment processing capabilities. These businesses, ranging from local boutiques to growing e-commerce stores, benefit from PayPal’s global reach and integrated financial tools, which facilitate smoother transactions and financial management.
Large Enterprises and Corporations: While not as numerous as SMBs, large enterprises form a crucial segment for PayPal, often integrating the platform’s payment solutions into their extensive operations. This includes multinational corporations seeking streamlined payment processes for their global customer base and B2B transactions.
Freelancers and Gig Economy Workers: With the rise of the gig economy, PayPal has become an essential tool for freelancers, independent contractors, and remote workers. This growing segment utilizes PayPal to receive payments from clients worldwide, appreciating the platform’s reliability and widespread acceptance in the global marketplace.
Non-profit Organizations and Charities: PayPal serves as a vital platform for non-profits and charities, facilitating donations and fundraising efforts. These organizations benefit from PayPal’s reduced transaction fees for charitable giving and its integration with various fundraising platforms, enhancing their ability to collect and manage donations efficiently.
Value Proposition – Paypal Business Model Canvas

Secure and Convenient Transactions: PayPal offers a robust, encrypted platform that enables users to conduct financial transactions with confidence, while simultaneously providing the convenience of storing multiple payment methods in one digital wallet, thereby streamlining the online payment process for both consumers and businesses.
Global Reach and Multi-Currency Support: With operations in over 200 markets and support for 25 currencies, PayPal facilitates international transactions, allowing businesses to expand their customer base globally and enabling individuals to send money across borders effortlessly, thus breaking down geographical barriers in financial interactions.
Buyer and Seller Protection: PayPal’s comprehensive protection policies for both buyers and sellers foster trust in online transactions, covering eligible purchases for buyers if items are not received or significantly different from described, while also safeguarding sellers against fraudulent chargebacks, thereby creating a more secure e-commerce ecosystem.
Integrated Financial Services: Beyond basic payment processing, PayPal offers a suite of financial services including working capital loans for businesses, credit lines for consumers, and cryptocurrency trading, positioning itself as a one-stop financial platform that caters to diverse financial needs and enhances user engagement.
Innovation in Mobile and Contactless Payments: PayPal continually evolves its services to meet changing consumer preferences, exemplified by its mobile app, QR code payments, and integration with various e-commerce platforms, ensuring that users can transact seamlessly across multiple channels and devices in an increasingly digital world.
Revenue Streams – Paypal Business Model Canvas

Transaction Fees: PayPal’s primary revenue source stems from transaction fees, which are charged when users send or receive money, with rates varying based on transaction type and location; for instance, standard rates for sellers receiving payments range from 2.59% to 3.49% plus a fixed fee, depending on the specific payment method used.
Cross-Border Transaction Fees: When facilitating international transactions, PayPal generates additional revenue through currency conversion fees and cross-border transfer charges, which can range from 3% to 4% above the standard exchange rate, capitalizing on its global presence and multi-currency support capabilities.
Merchant Services: PayPal offers a suite of business solutions, including PayPal Checkout, Braintree, and various point-of-sale systems, which not only generate revenue through usage fees but also strengthen PayPal’s position in the e-commerce ecosystem by providing comprehensive payment processing solutions to merchants of all sizes.
Value-Added Services: The company has diversified its revenue streams by offering additional financial products such as PayPal Credit, business loans, and the PayPal Cashback Mastercard, which generate interest income and interchange fees, thereby expanding its financial services footprint beyond mere payment processing.
Venmo Monetization: As Venmo, PayPal’s peer-to-peer payment app, continues to grow, the company has introduced revenue-generating features such as Instant Transfer fees and the Venmo Credit Card, effectively monetizing a previously free service while maintaining its popularity among users, particularly millennials and Gen Z.
Channels – Paypal Business Model Canvas

Digital Platforms: PayPal’s primary channel is its digital ecosystem, encompassing its website and mobile applications, which serve as the main interface for users to access a wide array of services; this digital-first approach has been particularly effective, with mobile payment volume accounting for approximately 45% of PayPal’s total payment volume in recent quarters.
Partner Integrations: By integrating its services with numerous e-commerce platforms, such as Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento, PayPal extends its reach to millions of online merchants and their customers, thereby creating a seamless payment experience across various online marketplaces and significantly expanding its user base.
In-Store Presence: Although primarily known for online transactions, PayPal has been expanding its physical presence through partnerships with point-of-sale providers and the introduction of QR code payments, which have gained traction, especially during the pandemic, allowing users to make contactless payments in brick-and-mortar stores.
Strategic Acquisitions: PayPal leverages acquisitions as a channel to expand its service offerings and user base; notable examples include the acquisition of Honey, a popular browser extension for finding and applying coupons, which has allowed PayPal to engage with consumers earlier in their shopping journey.
Developer Ecosystem: Through its Developer Portal and APIs, PayPal has created a robust channel for third-party developers to integrate PayPal’s payment solutions into their applications and services, fostering innovation and expanding PayPal’s reach across diverse digital environments and use cases.
Customer Relationships – Paypal Business Model Canvas

Self-Service and Automation: PayPal prioritizes self-service tools and automated systems, allowing users to manage their accounts, transactions, and issues independently through its digital platforms; this approach not only empowers users but also enhances efficiency, with the company reporting that over 80% of customer inquiries are resolved through self-service channels.
Personalized User Experience: Leveraging big data and AI, PayPal delivers personalized experiences to its users, tailoring product recommendations and financial insights based on individual transaction histories and behaviors; this data-driven approach has contributed to increased user engagement, with the average number of transactions per active account rising to 46.5 annually in recent reports.
Community Engagement and Education: PayPal fosters customer relationships through educational content, webinars, and community forums, which not only provide valuable information to users but also create a sense of community; the PayPal Community forum, for instance, has become a hub for peer-to-peer support and knowledge sharing among users.
Proactive Fraud Protection: By employing advanced fraud detection systems and offering buyer and seller protection programs, PayPal builds trust and long-term relationships with its customers; this commitment to security has contributed to PayPal’s high customer retention rates, with the company reporting over 400 million active accounts in recent financial disclosures.
Responsive Customer Support: While emphasizing self-service, PayPal maintains multiple channels for direct customer support, including phone, email, and social media, ensuring that complex issues are addressed promptly; the company’s focus on customer satisfaction is reflected in its consistently high Net Promoter Scores, which have remained above industry averages in recent years.
Key Activities – Paypal Business Model Canvas

Payment Processing and Transaction Management: At the core of PayPal’s business is its secure and reliable payment processing capabilities, which enable seamless transactions between buyers and sellers across various e-commerce platforms, mobile apps, and in-store environments, while also managing the complex backend operations to ensure the smooth flow of funds.
Risk Management and Fraud Prevention: Given the inherent risks associated with online payments, PayPal dedicates significant resources to developing and maintaining robust risk management and fraud detection systems, employing advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to identify and mitigate fraudulent activities, thereby instilling confidence in its users and safeguarding the integrity of its platform.
Product Innovation and Feature Development: Recognizing the importance of staying ahead of the curve in the rapidly evolving fintech landscape, PayPal consistently invests in research and development to introduce innovative products and services, such as its Buy Now, Pay Later solutions, cryptocurrency trading, and new payment methods, ensuring that it remains a market leader and meets the evolving needs of its diverse customer base.
Regulatory Compliance and Licensing: As a financial services provider, PayPal must navigate a complex web of regulations and licensing requirements across the numerous jurisdictions in which it operates; the company dedicates substantial efforts to monitoring and adhering to these regulatory frameworks, ensuring that its operations remain compliant and mitigating potential legal and reputational risks.
Data Analytics and Customer Insights: Leveraging the wealth of transaction data and user behaviour insights available within its platform, PayPal actively engages in data-driven decision-making, utilizing advanced analytics to better understand its customers, optimize its product offerings, and tailor personalized experiences, thereby enhancing user engagement and loyalty over the long term.
Key Resources – Paypal Business Model Canvas

Technological Infrastructure: At the core of PayPal’s operations is its robust, scalable, and secure technological infrastructure, which includes advanced payment processing systems, data centres, and a global network of servers, enabling it to handle millions of transactions seamlessly and maintain high availability for its users across the world.
Intellectual Property: PayPal has amassed a significant portfolio of patents, trademarks, and copyrights, which safeguard its proprietary technologies, algorithms, and brand identity, providing a strong competitive advantage and serving as a barrier to entry for potential rivals in the digital payments landscape.
Talent and Expertise: As a technology-driven financial services provider, PayPal relies heavily on its diverse and highly skilled workforce, including software engineers, data scientists, risk management specialists, and customer service professionals, who collectively drive innovation, ensure operational efficiency, and deliver exceptional user experiences.
Partnerships and Integrations: PayPal has forged strategic partnerships with a wide range of e-commerce platforms, merchant acquirers, and financial institutions, allowing it to seamlessly integrate its payment solutions into a vast network of digital environments and physical retail locations, thereby expanding its reach and accessibility to both consumers and businesses.
Brand Reputation and Trust: Decades of reliable service, security, and consumer protection have helped PayPal establish a strong brand reputation and high levels of trust among its user base, which is a crucial asset in the financial technology industry, where consumer confidence is paramount for long-term success and growth.
Key Partners – Paypal Business Model Canvas

E-commerce Platforms: PayPal has forged deep partnerships with leading e-commerce platforms, such as Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento, allowing seamless integration of its payment solutions into these digital marketplaces, which in turn enables merchants to offer their customers a trusted and convenient checkout experience.
Financial Institutions: PayPal collaborates with a network of banks, credit card issuers, and other financial service providers to facilitate transactions, expand its product offerings, and provide its users with additional financial services, such as PayPal Credit and the PayPal Cashback Mastercard.
Merchant Acquirers: By partnering with major merchant acquirers, such as Fiserv and Chase Merchant Services, PayPal enhances its ability to onboard and support a diverse range of merchants, ensuring that its payment processing capabilities are widely accessible to businesses of all sizes across various industries.
Technology Providers: To bolster its technological infrastructure and drive innovation, PayPal engages with leading technology companies, including cloud computing giants like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure, as well as specialized fintech firms, to leverage their expertise and integrate cutting-edge solutions into its platform.
Fintech Ecosystem: PayPal actively participates in the broader fintech ecosystem, forging partnerships with emerging financial technology startups, payment processors, and digital wallets, allowing it to stay ahead of industry trends, access new technologies, and potentially acquire or invest in promising ventures to expand its service offerings.
Cost Structure – Paypal Business Model Canvas

Transaction Processing Costs: As a payment service provider, PayPal incurs significant costs associated with the processing of financial transactions, including interchange fees, bank and card network charges, and transaction monitoring expenses, which collectively account for a substantial portion of its overall cost structure.
Technology and Infrastructure Investments: To maintain its technological edge and ensure the reliability and security of its platform, PayPal dedicates considerable resources to the development, maintenance, and scaling of its IT infrastructure, including data centres, software systems, and cybersecurity measures, which represent a significant ongoing operational expense.
Customer Support and Service Delivery: Providing a high level of customer service and support is a key priority for PayPal, leading the company to invest in robust call centres, self-service tools, and personalized assistance channels, all of which contribute to its cost structure as it strives to deliver exceptional user experiences.
Regulatory Compliance and Licensing: Operating in a heavily regulated financial services industry, PayPal must comply with a complex web of rules and regulations across multiple jurisdictions, incurring substantial costs related to legal counsel, audits, license fees, and penalties, which can significantly impact its overall cost structure.
Marketing and Advertising: To maintain its market leadership and attract new users, PayPal devotes considerable resources to marketing and advertising campaigns, spanning digital channels, traditional media, and strategic partnerships, which, although essential for growth, represent a significant component of the company’s cost structure.
Summary of Company Paypal Model Canvas
Conclusion on Paypal Business Model Canvas
In conclusion, PayPal’s comprehensive business model canvas illustrates its multifaceted approach to digital payments. By catering to a diverse customer base, offering a compelling value proposition, and leveraging a robust technological infrastructure and strategic partnerships, PayPal has established itself as a dominant player in the fintech industry. Its ability to generate revenue through various streams, while closely managing its cost structure and key activities, has enabled the company to maintain its competitive edge and continue driving innovation in the rapidly evolving digital payments landscape.

I’m Samin Yasar, currently working as a Brand Strategist for one of the world’s leading Prop Firms. I have a passion for content creation and dream of making my own film one day.






