Burger King Business Model Canvas 2024
With iconic flame-broiled burgers and a globally recognized brand, Burger King has grilled its way into becoming one of the world’s largest and most successful fast food empires. In this Burger King business model canvas, we will learn its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting fact!
The person who, Jeff Neimand, voices The Burger King in commercials was originally part of the boy band 98 Degrees in the late 1990s.
Burger King Competitors
McDonald’s | Wendy’s | Subway | Taco Bell | KFC | Chick-fil-A | Domino’s Pizza | Dunkin’ Brands | Starbucks | Dairy Queen | Papa John’s | Sonic Drive-In | Little Caesars | Arby’s
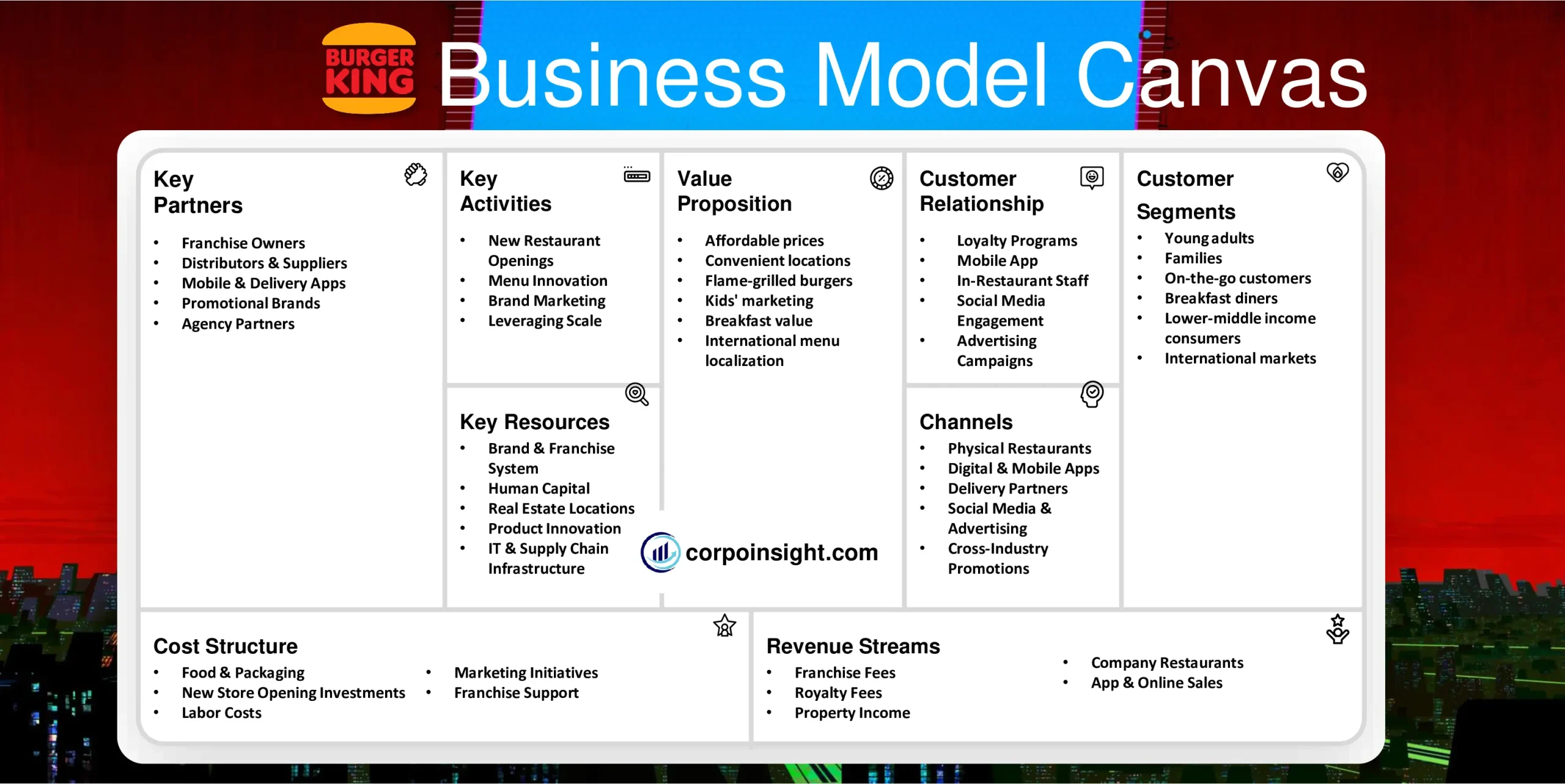
Customer Segments – Burger King Business Model Canvas

Young adults: Burger King targets adults aged 18-35 with affordable meal deals and modern marketing. In 2023, 58% of Burger King customers were under 35.
Families: Burger King positions itself as a family-friendly fast food chain, with kids’ meals and playgrounds in locations across the USA. About 29% of customers visit Burger King with children.
On-the-go customers: With drive-thru making up around 70% of sales, Burger King caters to people seeking quick and convenient meals, including office workers and commuters. Value menu items also attract these time-pressed customers.
Breakfast diners: Breakfast makes up 12% of Burger King’s sales, as they offer early opening hours and breakfast sandwiches/coffee for the morning meal.
Lower-middle-income consumers: Burger King focuses on price-based value menu items for mass-market, middle- and lower-middle-income consumers rather than premium products. The average customer has a household income under $60k.
Value Proposition – Burger King Business Model Canvas

Affordable prices: Burger King positions itself as a value-driven fast food chain with combo meals priced around $5-6 on average, 15-20% cheaper than competitors like McDonald’s. It also offers frequent coupons and specials.
Convenient locations: With over 18,300 locations globally, Burger King offers convenience for time-pressed diners. 70% of sales are drive-thru targeting on-the-go meals. Locations also often open earlier and close later than competitors.
Flame-grilled burgers: Burger King differentiates with flame-grilled burgers rather than griddled ones. Its ads focus on better burger taste, especially for core products like the Whopper. it appeals to young adult customers looking for a quick, tasty meal.
Kids’ marketing: By offering kids toys, games, and playgrounds, Burger King positions itself as kid- and family-friendly. For example, 10% of ads now target children to drive family visits.
Breakfast value: Burger King expanded breakfast menu options while keeping prices low with combo meals under $5. The breakfast value targeting commuters and parents fuels 12% of overall sales.
International menu localization: With 50% of locations outside North America, Burger King tailors regional menu options to local tastes. It includes veggie burgers in India and extra-large portions in Japan.
Revenue Streams – Burger King Business Model Canvas

Franchise Fees: Burger King generates over $500 million in revenue from initial franchise fees paid to open new restaurants. The current franchise fee is $50,000 per new location in the United States.
Royalty Fees: Burger King also collects monthly royalty payments from all franchisees based on 4-6% of gross sales revenue generated at each location. It makes up the majority of total revenue.
Property Income: Nearly all Burger King properties are leased to franchise owners who pay rent to the company. Burger King generates around $300 million in rental income.
Company Restaurants: While most locations are franchised, Burger King does operate some company-owned restaurants. These generate full restaurant sales and profits directly for corporations.
App & Online Sales: With mobile apps and online/digital channels growing, e-commerce is an emerging revenue stream. Digital and delivery sales are still a tiny but fast-growing percentage of total sales.
Channels – Burger King Business Model Canvas

Physical Restaurants: With over 18,300 locations, Burger King restaurant chains are the primary channel, comprising 70% drive-thrus targeting convenience & speed and 30% in-restaurant dining facilities.
Digital & Mobile Apps: Burger King apps & online ordering facilitate 10% of sales and growing, appealing to digitally-savvy young demographics. Features like Mobile Ordering and loyalty programs incentivize registered users.
Delivery Partners: By partnering with services like GrubHub, DoorDash, and Uber Eats, Burger King expands delivery options. Nearly 8,000 locations now offer delivery, increasing availability and convenience.
Social Media & Advertising: Burger King has over 11 million social media followers and invests heavily in new product ads on TV & digital platforms to drive brand awareness, especially with Gen Z & millennials.
Cross-Industry Promotions: Partnering with entertainment brands like Sony PlayStation and Xbox, Burger King uses innovative cross-promotions with prizes, rewards, and co-branded activations to expand reach into gaming culture and youth target markets.
Customer Relationships – Burger King Business Model Canvas

Loyalty Programs: Burger King’s Royal Perks loyalty program has over 20 million members who earn points for free food and other offers. It drives frequent purchases, with members visiting 25% more often.
Mobile App: The BK App features deals, customized offers, and mobile ordering to increase convenience. It has been downloaded over 21 million times, enabling direct customer engagement.
In-Restaurant Staff: With over 375,000 staff across chains, customer interactions with friendly and efficient in-store employees contribute significantly to the experience.
Social Media Engagement: By actively engaging followers across Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook, Burger King establishes brand personality with 36+ million social connections.
Advertising Campaigns: Ongoing cultural, entertainment, sports, and gaming partnerships combined with product promotions aim to attract younger demographics while establishing brand affinity across target customers.
Key Activities – Burger King Business Model Canvas

New Restaurant Openings: Burger King aggressively opens over 1,000 new restaurant locations each year globally. Store expansions into new markets, along with refreshing existing chains, fuels ongoing growth.
Menu Innovation: Burger King continually rolls out limited-time food offerings and product line extensions like chicken sandwiches, tacos, and breakfast options to drive interest and sales. In 2023, it introduced over 20 new menu items.
Brand Marketing: Burger King invests substantially in integrated marketing campaigns like awarding PS5 consoles with meal purchases. Such brand marketing partnerships combined with TV, digital, and sports advertising aim to attract younger demographics.
Leveraging Scale: With over 18,000 locations, Burger King leverages its global scale for cost savings. Recent deals with consolidated distributors and lock-in contracts with Coke and other major suppliers have reduced expenses.
Key Resources – Burger King Business Model Canvas

Brand & Franchise System: The fast-food hamburger Burger King brand and the well-established store franchising system are the business’s core assets, valued at $8.6 billion with 100% brand recognition globally.
Human Capital: Burger King has over 375,000 team members and restaurant staff worldwide, providing customer service and kitchen preparation skills to uphold operational standards. Ongoing training reinforces capabilities.
Real Estate Locations: Prime real estate locations of over 18,000 Burger King restaurants globally situated on major suburban roads enable customer accessibility and convenience for dine-in or drive-thru. 70% have drive-thrus.
Product Innovation: Burger King’s test kitchen facilities & product R&D infrastructure with over 1,000 restaurant partnerships enable rapid prototyping of new menu items. In 2023, 20 new products were test-launched systemwide.
IT & Supply Chain Infrastructure: Burger King deploys IT systems and supply chain infrastructure like proprietary point-of-sale tech, inventory management software, a distribution network of centers, and logistics fleets to enable operations.
Key Partners – Burger King Business Model Canvas

Franchise Owners: Burger King partners with hundreds of franchisees who own and operate over 90% of all locations. Franchisees invest in new unit growth in exchange for the use of Burger King’s brand, systems, and marketing support.
Distributors & Suppliers: Partners like McLane Logistics deliver to BK chains, while Restaurant Services Inc. serves as the exclusive Burger King distributor. Coca-Cola, Unilever, and Keystone Foods supply ingredients and materials at fixed rates.
Mobile & Delivery Apps: Integration partnerships with mobile apps like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and GrubHub have expanded BK’s delivery reach to 80% of locations. These facilitate growing digital sales channels.
Promotional Brands: Cross-promotions with gaming brands like Sony PlayStation and Microsoft Xbox fuse entertainment pop culture with the BK brand. These partnerships help attract younger consumers.
Agency Partners: Creative advertising agencies like David, MullenLowe, and Ingo handle local & global BK branding campaigns from concept to execution across media channels like TV and TikTok.
Cost Structure – Burger King Business Model Canvas

Food & Packaging: The highest costs for Burger King are ingredient and packaging expenses, including beef, chicken, buns, oils, and paper products. Due to scale, BK locks in low fixed pricing through exclusive supply contracts.
New Store Opening Investments: Burger King and its franchisees invest an estimated $300k-$2.5 million per new restaurant opening in development costs like real estate, equipment, and furnishings, depending on location.
Labor Costs: With over 375,000 global employees, labor is a major cost. However, Burger King keeps labor costs low in stores through training and technology investments like order point-of-sale systems.
Marketing Initiatives: Major advertising buys across TV, digital platforms, and sponsorships, plus product innovation testing, represent sizable marketing expenses aimed at brand awareness and customer acquisition.
Franchise Support: Providing franchisees with ongoing operational support for functions like training, analytics, marketing, and monitoring team service levels requires corporate headquarters investments.
Summary of Burger King Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on Burger King Business Model Canvas
Burger King has built a highly successful fast food empire by utilizing its iconic flame-grilled burger brand appeal and a robust franchising model to achieve substantial global scale and presence. It maintains a laser focus on convenience, speed of service, and affordability for its target mass consumer markets. Through innovation, promotions, digital channels, and win-win partnerships, Burger King strives to deepen customer relationships and drive increased visits to its growing restaurant chains worldwide.

Hi! I am Mohammad Safayet Hossain, pursuing my BBA in Marketing at the Bangladesh University of Professionals. As a business student, I am passionate about learning about various companies and industries and am here to share them with you.







