Starbucks Business Model Canvas 2024
Starbucks has made its name as the most available and found place all around the world, and anywhere you go, you will find a Starbucks right around the corner. We will learn all about Starbucks in this Starbucks Business Model Canvas, along with its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting Facts!
There’s a “secret” Starbucks menu that includes off-the-board colorful drinks like a Cotton Candy Frappuccino, Tie-Dye Frappuccino, and even a Cap’n Crunch Frappuccino for the cereal lovers.
Starbucks Competitors
Dunkin’ (Dunkin’ Donuts) | Costa Coffee | Tim Hortons | McCafé (McDonald’s) | Peet’s Coffee & Tea | Caribou Coffee | The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf | Caffè Nero | Lavazza | Nespresso
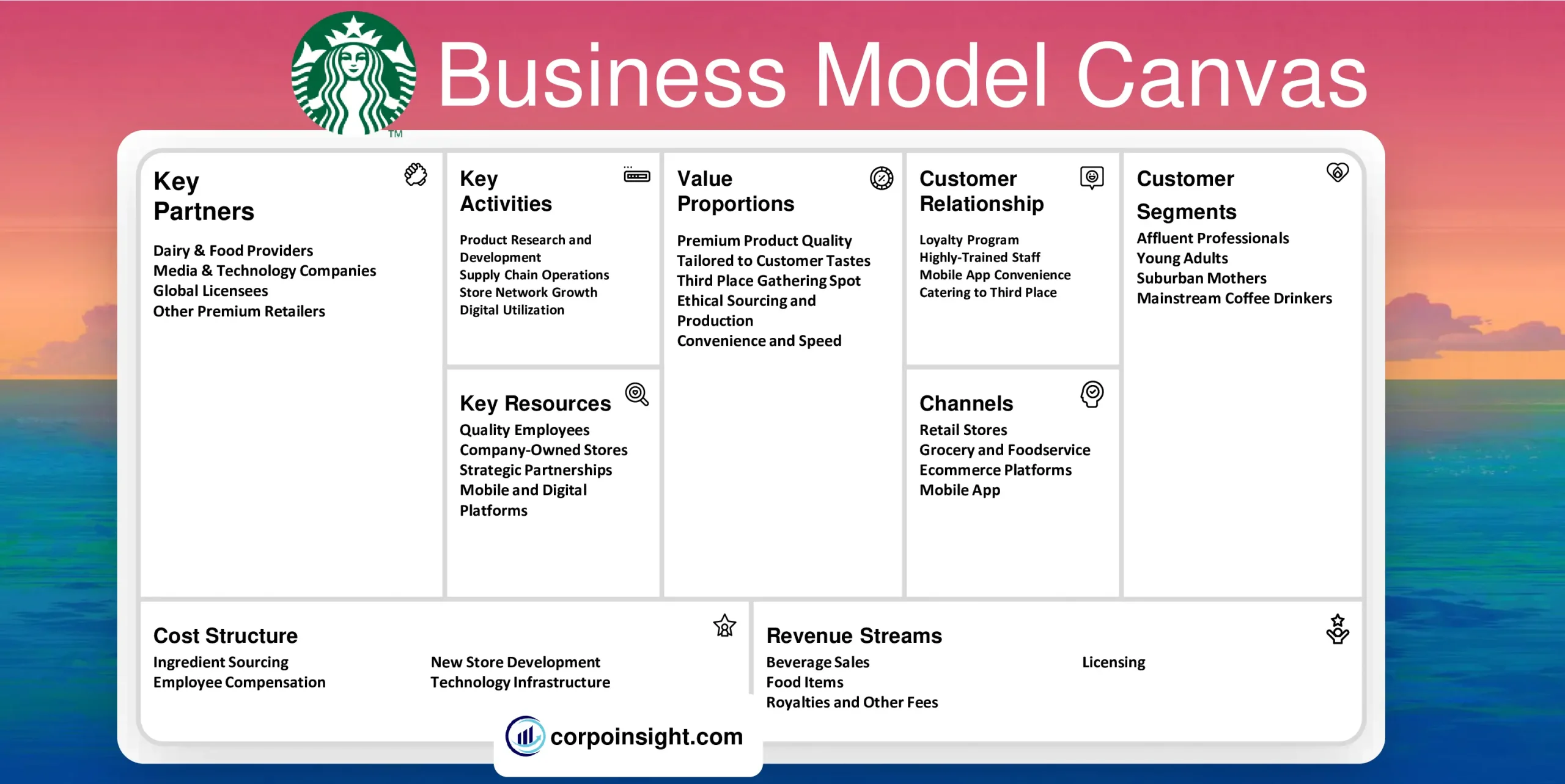
Customer Segments – Starbucks Business Model Canvas

Affluent Professionals: This customer segment, making up 40% of sales, includes college-educated professionals with above-median incomes seeking premium beverages for work breaks or casual gatherings. Starbucks positions itself as an affordable luxury for this group through its ambiance and status beverages.
Young Adults: Representing 35% of customers, students, and young professionals under 30, frequent Starbucks as an informal gathering place and workspace. Starbucks attracts them through discounted campus offers, happy hours, and mobile ordering convenience geared to those who are always on the go.
Suburban Mothers: This key segment makes up 15% of traffic, stopping at Starbucks for a brief respite from shuttling kids to activities and connecting with friends. Starbucks provides a comfortable haven and leverages this group’s interest in customization, offering specialized drinks.
Mainstream Coffee Drinkers: Predominantly middle-aged commuters comprise 10% of customers, drawn more by habit, speed, and value than ambiance. Starbucks retains them through cost-saving loyalty program rewards and routine AM coffee runs via the efficient Drive Thru.
Value Proposition – Starbucks Business Model Canvas

Premium Product Quality: Starbucks offers fresh-roasted whole-bean coffee and handcrafted espresso beverages, baked goods, sandwiches, and protein meals prepared daily. Starbucks invests heavily in quality ingredients, roasting overseas-sourced Arabica coffee in its US facilities.
Tailored to Customer Tastes: With over 87,000 drink combinations, Starbucks allows for hyper-customization to accommodate consumers’ unique preferences. Over 21% of orders are customized, enabled by extensive barista up-training.
Third Place Gathering Spot: With over 35,000 locations globally, Starbucks aims to be an inviting space between one’s work and home for connection or focus. Stores feature lounge areas, free wi-fi, and outlets welcoming customers to linger.
Ethical Sourcing and Production: Starbucks has comprehensive guidelines for producing and procuring coffee sustainably, supporting farmer loans and forest conservation. 75% of coffee is ethically sourced under these “Coffee and Farmer Equity” practices.
Convenience and Speed: With innovations like Mobile Order & Pay launched in 2015, now representing 25% of US orders, and multi-store loyalty rewards, Starbucks facilitates easy access to one’s desired beverage and food on the go.
Revenue Streams – Starbucks Business Model Canvas

Beverage Sales: Revenue from hot, iced, and blended beverage purchases totaled $17.67 billion, accounting for 75% of company-operated store sales in 2021. Coffee drinks and teas still reign as Starbucks’ main source of income.
Food Items: Food constituted 25% of store sales – or $5.92 billion last fiscal year. Breakfast sandwiches, bakery items like cake pops and cookies, lunch foods, and snack bags all contribute to food income, which is especially important for non-peak hours.
Royalties and Other Fees: Money accrued from royalties and ad funding from foreign partners totaled nearly $1.7 billion as Starbucks continued its global expansion in 2021. Over 32,000 stores now operate overseas, paying initial build-out and ongoing royalty fees.
Licensing: Consumers encounter Starbucks products for in-home use through partnerships worth $2.2 billion in CPG goods like coffee beans for Keurig brewers or Starbucks Doubleshot canned drinks and premium ice creams sold in grocery aisles globally.
Channels – Starbucks Business Model Canvas

Retail Stores: With over 15,000 US and 32,000 global locations, company-owned and licensed stores enable customers to purchase in person. Stores drive 78% of revenue through walk-in, drive-thru, curbside, and Mobile Order & Pay methods.
Grocery and Foodservice: Starbucks sells packaged coffee, teas, and ready-to-drink beverages to grocery outlets, business offices, hotels, hospitals, and college campuses. These partnerships accounted for $2.7 billion in sales last year.
E-commerce Platforms: Customers can order Starbucks products to be shipped directly to them through partnerships with Amazon, Instacart, Postmates, and Uber Eats in select markets. Subscriptions for automatic coffee or K-cup pod deliveries are available online.
Mobile App: With 26.4 million US reward members and a world-class app, Starbucks encourages mobile pre-orders and payment for pickup or delivery. Over a quarter of US company-operated sales are mobile –equating to 9% incremental revenue gains.
Customer Relationships – Starbucks Business Model Canvas

Loyalty Program: With 26.4 million US members, Starbucks Rewards enables personalized offers and prompts purchases through points and freebies. Members contribute over 50% of sales, visit more often, and spend more per trip, driving significant revenue.
Highly-Trained Staff: By investing in training programs like the Starbucks College Achievement Program, employees can provide a positive human connection during each visit. Customers return for the fast service and customized care from baristas who may remember their usual.
Mobile App Convenience: Ordering and paying via Starbucks’ mobile app, adopted by 36% of loyalty members, provides an efficient yet customized experience. Customers can find nearby stores, order and pay ahead to save time, access rewards, and review purchase history and preferences.
Catering to Third Place: From lounge-like stores to free wi-fi and charging outlets, Starbucks locations invite customers to treat the space like a relaxing public living room to facilitate meaningful community connections.
Key Activities – Starbucks Business Model Canvas

Product Research and Development: Starbucks continually innovates new beverages, food items, preparation methods, and store formats. With its Tryer Center and $850M annual R&D budget, Starbucks develops category-leading items like cold foam drinks, plant-based options, and holiday beverages.
Supply Chain Operations: To ensure access to premium, sustainably sourced Arabica beans, Starbucks manages highly integrated supply lines spanning growers in 30 countries, strategic inventory/shipping, and locked-in future purchase contracts changed daily based on forecasts.
Store Network Growth: Starbucks accelerates new retail location development – prioritizing high-traffic spots while closing some lower-volume stores. Over 3,100 new stores opened in 2021 alone, now spanning 33,833 global retail and license store locations in over 83 markets.
Digital Utilization: Through initiatives like model food ordering, personalized marketing, and customization memory, Starbucks optimizes digital channels to facilitate faster service, boost loyalty program engagement to 26.4 million members, and drive 36% of sales from pre-order mobile pickup.
Key Resources – Starbucks Business Model Canvas

Quality Employees: With 383,000 employees, Starbucks invests substantially in training programs like Starbucks College Achievement to foster expert baristas and committed store managers who provide premium customer service. Employees receive full benefits even as part-timers.
Company-Owned Stores: Starbucks owns over 15,000 of its retail locations globally, prioritizing key metros and high-traffic spaces. Controlling real estate assets enables testing innovations and showcasing the Starbucks brand experience through careful atmosphere and design choices.
Strategic Partnerships: Licensing partnerships spanning 190,000+ retail and grocery points bring Starbucks brand exposure while supplying revenue streams. Nestle at-home coffee, PepsiCo bottled drinks, and Delta Airlines in-flight offerings all expand Starbuck’s presence.
Mobile and Digital Platforms: With industry-leading app engagement among loyalty members and technology like AI-powered drive-thrus, Starbucks facilitates personalized, efficient ordering. Digital tools and integrated PoS systems enable operations while collecting customer data.
Key Partners – Starbucks Business Model Canvas

Dairy and Food Providers: Starbucks partners with producers like Danone, Alpro, and Evolution Fresh for items from milk, juice, and yogurt to breakfast sandwiches and protein boxes, ensuring supply for 25% of the food revenue share from 15,000+ stores.
Media and Technology Companies: Partners like The New York Times, Spotify, and Apple enable in-store digital access for news, music, and payments. Software firms support back-end tech infrastructure as mobile orders exceeded 26% of transactions, contributing over $4 billion annually.
Global Licensees: With 7,000+ international licensed stores from Mexico to South Korea operated by partners, Starbucks taps local expertise while collecting royalties. Diverse operations under the Starbucks brand boost reach and access emerging markets earlier.
Other Premium Retailers: Strategic brand partnerships facilitate shared customer bases across companies like Anthropologie, Levis, and the New York Times, promoting Starbucks with aligned premium, progressive brand images for mutual benefit.
Cost Structure – Starbucks Business Model Canvas

Ingredient Sourcing: Premium, ethically sourced Arabica coffee beans comprise Starbucks’ greatest input cost, fluctuating based on global supply and contributing 12% of revenue. Dairy, produce, meats, and bakery items also drive up food revenue share. Direct and long-term grower relationships secure supply.
Employee Compensation: From renowned benefits even for part-timers to training programs like Starbucks College Achievement, the 383,000+ employee support nets higher retention for better customer service. Labor still constitutes nearly 30% of store operating expenses in Starbucks’ service-intensive model.
New Store Development: As Starbucks accelerates expansion entering new markets, store operating costs from construction, design testing and market research require substantial capital investment offset by focusing on densely-populated metro locations to maximize revenue.
Technology Infrastructure: With industry-leading app adoption and digital channel prioritization, Starbucks invests significantly in CRM databases, synthesizing customer data for personalization and AI-powered ordering and customization to capture additional revenue by added convenience.
Summary of Starbucks Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on Starbucks Business Model Canvas
Starbucks dominates the specialty coffeehouse segment by offering premium handcrafted beverages and quality food enabled by company-owned store networks located on high-traffic real estate. Starbucks drives habitual customer visits by leveraging industry-leading loyalty rewards program convenience, customization options, consistency in service through considerable employee investments, and adapting innovations in consumer digital technology – together fueling steadily growing revenue streams over its 50-year history.

Majoring in marketing from Bangladesh University of Professionals, Sadman Abrar is a learner, obsessed with branding and intrigued to learn about different company strategies, and currently working at bKash.