Uber Business Model Canvas 2024
Uber has disrupted the transport industry in a big way, opened up to so many ideas, and inspired young entrepreneurs to go after those disruptive ideas you can’t even count. In this Uber business model canvas, we will learn its customer segments, value proposition, revenue streams, channels, customer relationships, key activities, key resources, key partners, and cost structure.
Interesting Facts!
Uber’s wackiest service ever offered was UberCHOPPER, which, for $3,000, would hire a personal helicopter to pick you up and drop you off in New York City.
Uber Competitors
Lyft | Didi Chuxing | Ola | Grab | Gett | Curb | Via | Careem | Juno | Bolt
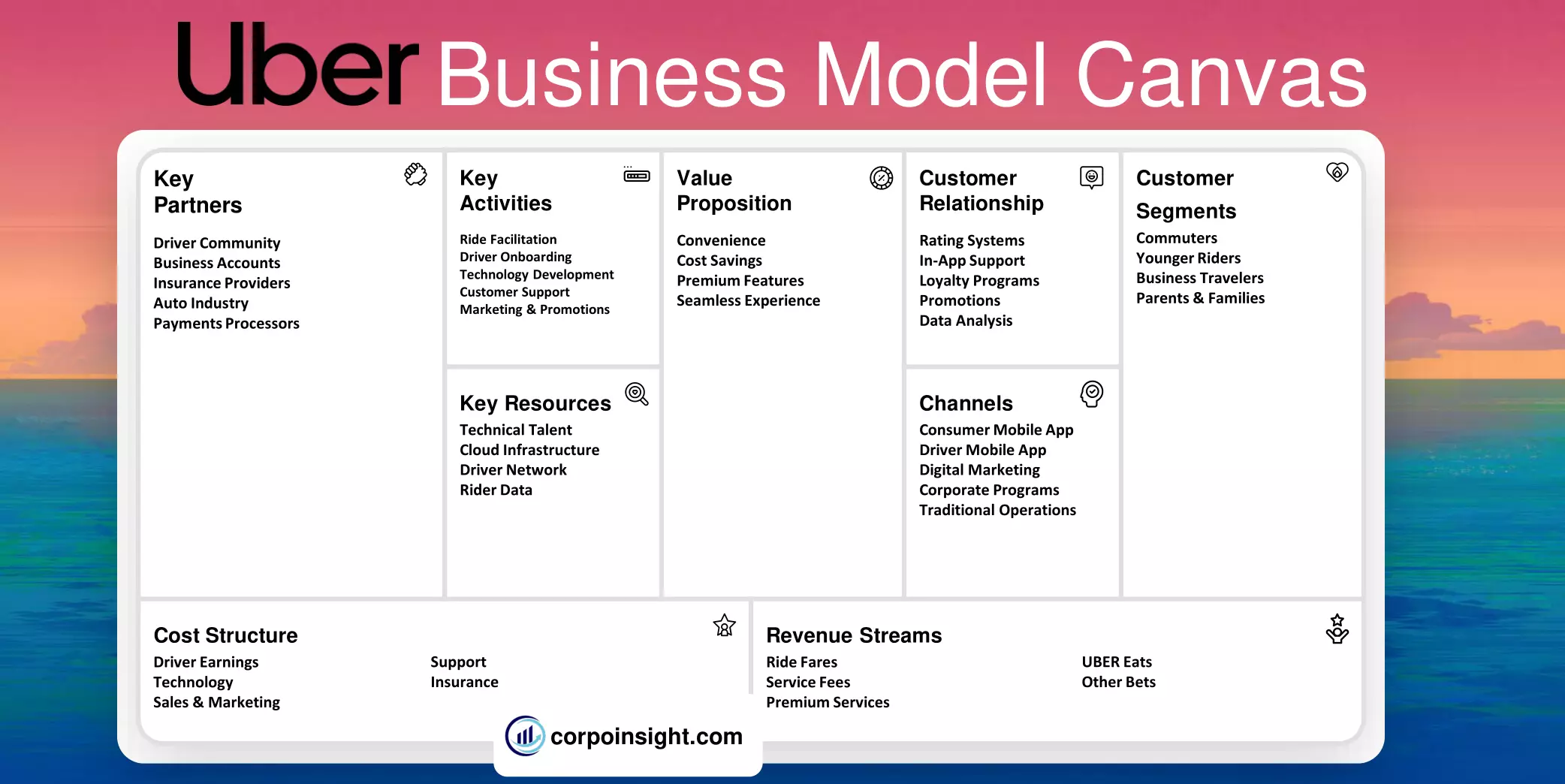
Customer Segments – Uber Business Model Canvas

Commuters: One of Uber’s largest groups, commuters rely on Uber for convenient rides to work and back. Uber estimates over 15 million trips per day are commuting trips. Many switch from public transport to the comfort, predictability, and time-savings of rideshares.
Younger Riders: Over 40% of Uber’s riders are aged 16-34, and as fewer young people own cars nowadays, on-demand rides provide freedom. For digital natives, hailing one via an app is second nature. Events, nights out, and trips across town are common uses.
Business Travelers: Frequent fliers who need transport while away on business trips or meetings comprise a revenue-rich segment. Over 25% of Uber trips are for business, attracted by easy expensing, consistency, and higher-end options like Uber Black.
Parents and Families: Uber provides family transportation, from parents managing kids’ activities to groups traveling together. Features like car seats and family profiles offering oversight help address safety concerns.
Value Proposition – Uber Business Model Canvas

Convenience: Uber is available in over 10,000 cities globally, with 3.9 million drivers providing rides around the clock. With just a few taps, a ride can be secured rapidly, avoiding taxi stand waits or public transit woes. This ease of use and reliability is a prime appeal.
Cost Savings: By leveraging non-professional drivers using their own vehicles, Uber offers average savings of around 30% compared to traditional taxi services. Dynamic pricing adjusts fares to demand, with special hourly rates, carpooling, and promotions further decreasing costs.
Premium Features: For business travelers and those seeking higher-end vehicles, Uber Black, Black SUV, and Taxi cater to premium needs. Features like leather seats, professional chauffeurs, and bottled water distinguish these tiers at a premium fare price.
Seamless Experience: From in-app ride tracking to driver details to cashless payments and digital receipts, Uber delivers a technologically streamlined user experience. Ratings enable accountability on both sides. The app also increases safety and efficiency versus e-hailing alternatives.
Revenue Streams – Uber Business Model Canvas

Ride Fares: Uber generates most revenue by taking a 20-25% commission from fares on each ride. With over 19 million trips daily globally, this commission nets billions annually. Regionally, over $10 billion in gross bookings comes from the US/Canada alone.
Service Fees: Riders also pay a small booking fee per trip, ranging from $0.99 to $2.99 depending on trip cost. At billions of trips per year, these minor fees accumulate significantly, exceeding $800 million annually.
Premium Services: Options like Uber Black, SUV, Lux, and platform access fees for business profiles also generate strong revenue. Globally, over 15% of trips use premium categories with higher margins.
UBER Eats: Uber’s food delivery vertical takes a 30% cut of meal receipts, contributing over $44 billion in gross bookings last year. While smaller than rides, UBER Eats is among the fastest-growing revenue streams.
Other Bets: Emerging segments like freight shipping, financial services for drivers, and autonomous vehicles represent future revenue sources still in development or early stages.
Channels – Uber Business Model Canvas

Consumer Mobile App: Uber’s primary customer channel is its mobile app, which is available on iOS and Android. This enables on-demand ride-hailing, cuts costs of phone support, and provides direct customer relationships. Seamlessly integrated maps, payments, and communication maximize convenience.
Driver Mobile App: The driver app mirrors rider functionality – drivers can instantly receive and manage trip requests nearby through the app. This two-sided model keeps a dynamic supply of drivers available to fulfill demand where and when it arises.
Digital Marketing: To attract new consumers and drivers, Uber relies heavily on online marketing across search, display ads, and social media. Referral programs leading to account credits incentivize viral growth. As a mobile-first platform, much activity goes directly or through app stores.
Corporate Programs: Over 40% of Uber rides are business trips facilitated through corporate and business profiles. Companies manage employee access and payment to enable frictionless work travel. Uber partners directly with numerous global corporations to drive this segment.
Traditional Operations: Though app-based virtually, Uber maintains physical support through Greenlight hubs for in-person accounts, vehicle inspection, and driver assistance. Traditional branding, like billboards and sponsorships, raises wider awareness.
Customer Relationships – Uber Business Model Canvas

Rating Systems: Uber employs a two-way rating system for customers and drivers to evaluate each experience out of 5 stars. This enables accountability, quality control, and performance standards – low ratings lead to penalties or account deactivation on either side.
In-App Support: The Uber app provides self-serve help resources like FAQs, safety information, and account management. If needed, users can easily connect to 24/7 live chat, email, or phone support from within the app for a seamless experience.
Loyalty Programs: Frequent riders can enroll in membership programs like Uber Rewards to earn perks like flexible cancellations or priority airport pickups.
Promotions: First-time users often get promotions, adding credits to encourage adoption. Special personalized or location-based discounts maintain engagement, especially amongst casual riders.
Data Analysis: With detailed digital records of all rides and behaviors in its ecosystem, Uber leverages big data and analytics to optimize operations as well as tailor marketing per rider. This enables precision targeting amidst a wealth of customer insights.
Key Activities – Uber Business Model Canvas

Ride Facilitation: Uber’s central activity is enabling seamless urban transportation by matching riders to drivers and coordinating end-to-end ride provision. Complex algorithms quickly match demand to supply across over 10,000 cities, with over 19 million trips daily.
Driver Onboarding: To expand capacity, Uber focuses heavily on acquiring new drivers through promotions, referrals, and streamlined signup flows. Applicants complete identity checks and vehicle inspections to meet safety standards.
Technology Development: With over 3,000 engineers, Uber continually enhances its apps, dispatch algorithms, data analytics, mapping integrations, and payment platforms. This maintains quality standards and competitive differentiation on both rider and driver-facing tech.
Customer Support: Uber maintains 24/7 customer service via in-app messaging, phone, and email, covering ride issues, safety concerns, billing questions, and account management. Support resources like FAQs, insurance info, and community forums supplement direct assistance.
Marketing & Promotions: Boosting adoption among riders and drivers is crucial, relying on digital advertising, personalized promotions like credits or dynamic discounts, and referral rewards programs. Uber analyzes data to optimize spending and conversion rates.
Key Resources – Uber Business Model Canvas

Technical Talent: With over 4,000 IT professionals, including engineers, developers, AI experts, and data scientists, Uber relies on premier tech talent to maintain and optimize its digital infrastructure and apps. This drives innovation to enhance user experiences.
Cloud Infrastructure: Uber leverages Google Cloud, AWS, and Oracle Cloud for its computing, storage, database and analytics capabilities. Cloud scalability supports real-time coordination of millions of daily rides globally.
Driver Network: The 3.9 million Uber drivers providing services across international markets are a vital decentralized resource. Onboarding more drivers enables rising demand fulfillment, optimized by algorithms matching supply to riders.
Rider Data: With detailed records of over 118 million monthly active platform users, Uber gains valuable data on rider behavior, movement patterns, and service usage to inform pricing, promotions, and expansion decisions.
Key Partners – Uber Business Model Canvas

Driver Community: The vast network of contracted driver-partners is essential for providing rides at scale. Incentive programs and a flexible earnings model maintain this ecosystem of over 5 million non-employee drivers globally.
Business Accounts: Over 40% of Uber trips are corporate rides from business partnerships. Companies manage employee access, consolidated payments, and reporting for streamlined expense reporting across entire organizations.
Insurance Providers: To cover potential risks across billions of rides annually, Uber partners with diversified insurance companies globally. Policies protect both drivers and riders according to local regulations in each operating region.
Auto Industry: Vehicle rental and purchase programs offer special deals helping drivers obtain cars to provide services. Uber also partners with automakers on data sharing and electric vehicle efforts to shape future transportation infrastructure.
Payments Processors: Seamless, cashless payments rely on deep integrations with payment networks like Visa, Mastercard, and PayPal across Uber’s apps and driver disbursement systems. These ensure efficient, reliable transaction clearing at an immense scale.
Cost Structure – Uber Business Model Canvas

Driver Earnings: The largest cost is payouts to contracted drivers, making up over 70% of Uber’s ride revenue. This maintains a robust supply of independent drivers to meet ride demand without incurring employee costs.
Technology: With thousands of technical employees and cloud infrastructure to support complex real-time coordination algorithms, Uber spends over 15% of bookings on developing and supporting its apps and platform.
Sales and Marketing: User acquisition and retention includes considerable incentives, promotions, referrals, and advertising – especially amidst strong rivals. Uber seeks to maximize return on these outlays through data analytics.
Support: Though partly outsourced abroad, the in-house staff handles 24/7 phone, email, and chat support across 8 global hubs. This demand-driven expense enhances customer satisfaction but adds overhead.
Insurance: To cover rides drivers and mitigate risks, insurance partnerships are critical operationally. Policies meeting local rideshare regulations maintain safety assurances but comprise another variable cost layer.
Summary of Uber Business Model Canvas
Conclusion on Uber Business Model Canvas
Uber’s business model centers around its ridesharing platform and mobile app technology, which seamlessly connects riders and drivers for on-demand urban transportation. By taking a commission on over 19 million trips daily while minimizing asset ownership, Uber leverages efficiencies of scale and smart automation to pioneer a vast, convenient service at reduced prices compared to taxis. Though sustaining massive losses financially, the platform continues seeing steep usage growth, benefiting from and evolving with smartphone adoption habits. Ultimately, Uber’s value lies in transforming point-to-point mobility.

Hi! I am Mohammad Safayet Hossain, pursuing my BBA in Marketing at the Bangladesh University of Professionals. As a business student, I am passionate about learning about various companies and industries and am here to share them with you.